CONCEPT
2025
Integrated
Integrated
native sharing to eliminate user friction in key flow
native sharing to eliminate user friction in key flow
CONCEPT
2025
USER-EXPERIENCE Design
Case Study
Mobile


Role
Lead Designer
Team
1 Designer
Timeline
January – February 2025
Skills
UX Design, Research
Mobile App
Modals
B2C
Role
Lead Designer
Team
1 Designer
Timeline
Jan – Feb 2025
Skills
UX Design
Research
CONTEXT
CONTEXT
External sharing disrupted listening
External sharing disrupted listening
Spotify does not support in-app music sharing, requiring users to rely on external links or third-party messaging to share what they’re listening to. This project focuses on introducing native music sharing to reduce disruption, and make music sharing a natural extension of the product experience.
Spotify relies on external links or third-party apps for sharing. This creates friction in what should be a seamless listening behavior.
Note: The native sharing capabilities explored in this case study have since been reflected in Spotify’s product updates, supporting the long-term viability of the direction proposed.
Note: Spotify introduced similar native sharing features in May 2025, validating the direction explored in this case study.
IMPACT
IMPACT
Streamlined music sharing experience
Streamlined music sharing experience
Introducing in-app music sharing streamlines how users share what they’re listening to by removing the need to leave Spotify or rely on external platforms. The new simplified sharing flow reduces cognitive load and friction, making it faster and easier for users to share music in the moment. This increases the likelihood of sharing and supports higher engagement around shared content.
Introducing in-app sharing removes the need to leave Spotify and reduces friction in the sharing process. The simplified flow makes music easier to share in the moment and supports higher engagement around shared content.
PRODUCT SHOWCASE













OUTCOMES
Faster Sharing
when sharing a song in testing.
Clearer Flow
when completing sharing steps.
Higher Intent
when using native sharing feature.
PRODUCT SHOWCASE






OUTCOMES
Faster Music Sharing
comparing time to share across external and in-app sharing flows.
Better Flow Clarity
measured through faster completion across task-based usability testing.
Higher Sharing Intent
based on user-reported likelihood to share music using native sharing.
PROBLEM DEFINITION
PROBLEM DEFINITION
Core sharing flow breaks engagement
Core sharing flow breaks engagement
Despite Spotify’s growing investment in social features, sharing music remains unnecessarily difficult within the app. Users who want to share music are pushed to do so externally, increasing the cognitive overload. This undermines a core behavior and limits how often users share and engage around music.
Despite new social features, sharing music on Spotify still requires leaving the app. This adds friction to a core behavior and limits engagement around music.
Hypothesis: If song sharing is supported natively within Spotify through a clearer, lower-friction flow, users will share more frequently and engage more with shared content.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
How do Spotify listeners currently share music?
Sharing & Behavior
What issues prevent more frequent music sharing?
Pain Points & Barriers
Do these issues impact app social engagement?
Engagement & Interaction
How do listeners share music?
Sharing & Behavior
What prevents more frequent sharing?
Friction & Barriers
Do these issues impact engagement?
Engagement & Use
Hypothesis: Increasing intent and accountability would improve follow-through and retention.
OBSERVING USERS
OBSERVING USERS
Examining real-time sharing behavior
Examining real-time sharing behavior
I conducted a contextual inquiry with 12 active Spotify users to observe how music sharing unfolds within real listening routines. Watching users attempt to share songs in the moment exposed structural friction in the current flow, including additional steps, app switching, and hesitation at the point of intent. These observations clarified where the product diverges from natural sharing behavior.
I observed twelve active users sharing music within real listening routines. This exposed consistent breakdowns where the flow diverged from natural behavior.
CONTEXTUAL INQUIRY








CONTEXTUAL INQUIRY




KEY PAIN-POINTS
KEY PAIN-POINTS
Broken Flow
External sharing adds unnecessary steps that interrupt listening and overall experience.
Cognitive Overload
Leaving the app to share music breaks context and intent, thus weakening engagement with content.
Discouraged Sharing
Higher friction adds to hesitation at the point of sharing, making repeat sharing more unlikely.
Broken Flow
External sharing adds several unnecessary steps that interrupt listening and overall experience.
Cognitive Overload
Leaving the app to share music breaks context and intent, thus weakening engagement with content.
Discouraged Sharing
Higher friction adds to hesitation at the point of sharing, making repeat sharing more unlikely.
UNDERSTANDING USERS
UNDERSTANDING USERS
Understanding friction through surveys and interviews
Understanding friction through surveys and interviews
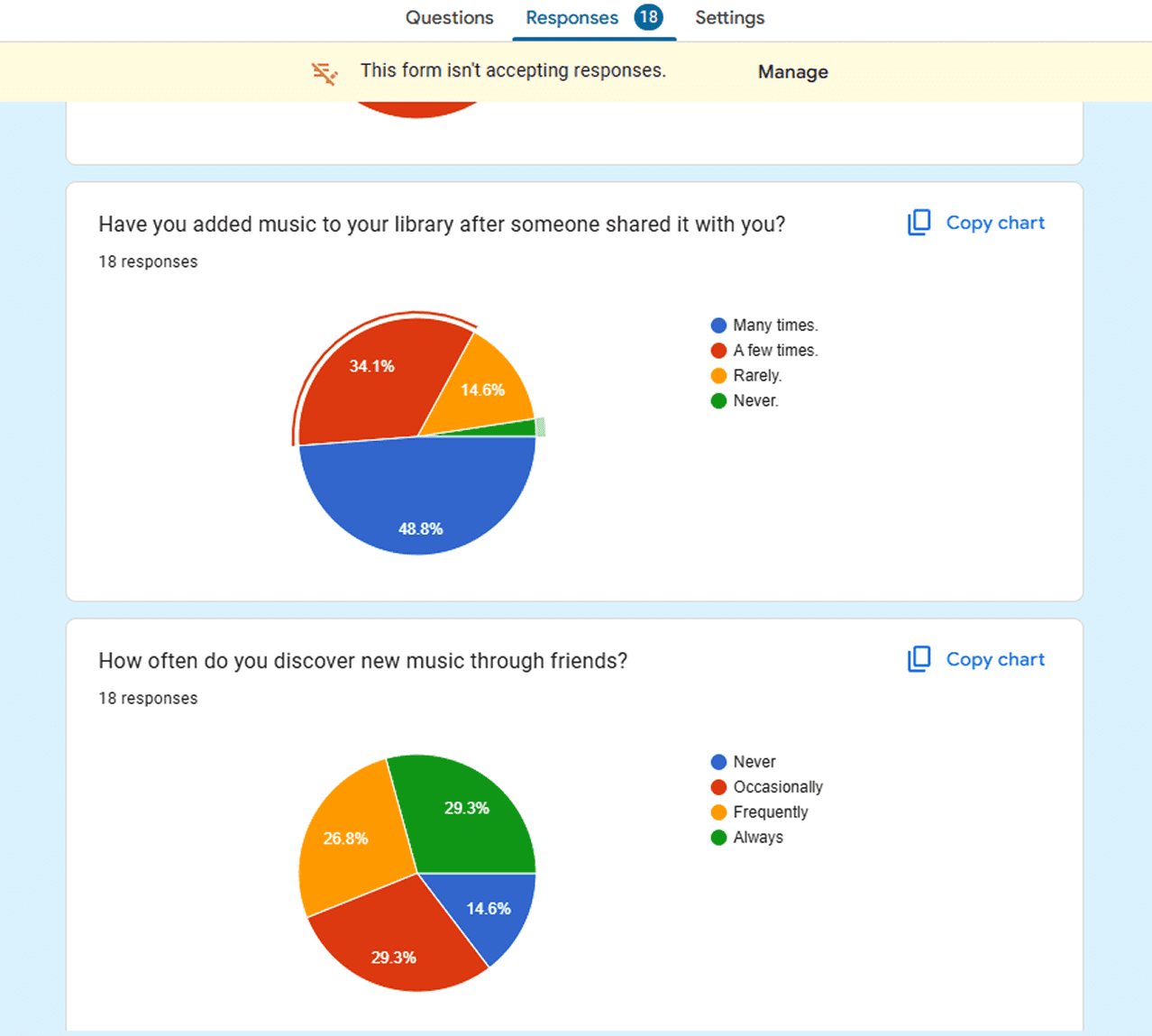
Following these observations, I conducted open-ended interviews and a survey with 18 active Spotify users to understand motivations behind sharing. While the contextual inquiry revealed where friction occurs, this phase focused on why users share, what outcomes they expect, and how sharing supports connection and discovery. This clarified the underlying behavioral intent driving sharing.
I conducted interviews and a survey with 18 active Spotify users to understand motivations behind sharing. This phase focused on why users share and what they expect from the interaction.
USER SURVEY
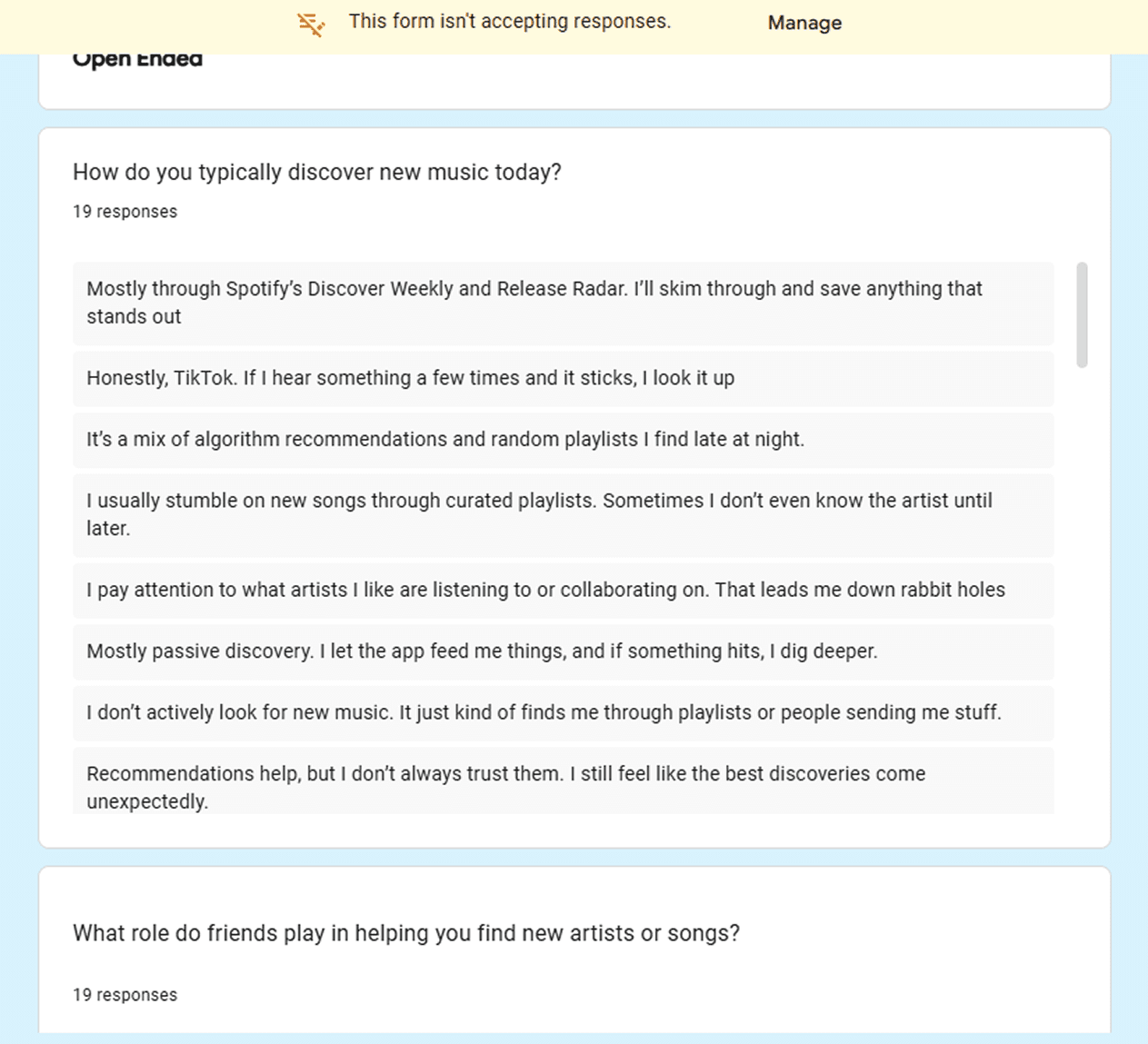
INSIGHTS
INSIGHTS
Social Interaction
Users often share music to start social interactions.
Discovery Catalyst
Shared music drives discovery beyond app recommendations.
Trusted Curation
Friends’ recommendations carry more weight than algorithms.
Interaction
Users often share music to socialize.
Discovery
Shared music often drives discovery.
Curation
Recommendations carry more weight.
USER SURVEY




COMPETITOR ANALYSIS
COMPETITOR ANALYSIS
Examining competitive interaction models
Examining competitive interaction models
With user intent clarified, I analyzed Apple Music and YouTube Music to understand how leading platforms structure music sharing. While collaboration features do exist, sharing is not embedded within core interaction flows. Apple relies on iOS-level integration through iMessage, whereas YouTube Music mirrors Spotify’s link-based model, reinforcing the off-platform friction users describe.
I analyzed Apple Music and YouTube Music to evaluate how leading platforms approach music sharing. While collaboration features exist, sharing is not embedded within core interaction flows, reinforcing similar off-platform friction.

Spotify
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening

Apple Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening

Youtube Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening
Key Insight: Across dominant platforms, sharing is treated as a peripheral feature rather than an integrated interaction layer within core user flows.
Key Insight: Across dominant platforms, sharing is treated as a peripheral feature rather than an integrated interaction layer.


Spotify
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening


Apple Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening


Youtube Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening
IDEATION
IDEATION
Establishing solution architecture
Establishing solution architecture
Building on the research, I re-engaged the same 12 users from the contextual inquiry in a focused workshop to evaluate structural approaches to in-app sharing. Flow testing clarified where sharing should live and how many steps felt acceptable at the point of intent. Feature prioritization ensured the direction remained lightweight, avoiding the complexity that previously limited adoption.
I re-engaged the same twelve users in a workshop to evaluate structural approaches to in-app sharing. Flow testing clarified optimal entry points, while feature prioritization kept the solution lightweight and focused.
WORKSHOPPING SESSION
HMW: How might we enable in-app music sharing that feels effortless in the moment, without increasing product complexity or disrupting listening?
FEATURE SIGNALS
FEATURE SIGNALS
Native Solution
Sharing must be embedded within Spotify’s core listening experience.
Effortless Action
Sharing must feel immediate and does not interrupt listening.
Focused Scope
Enhances listening without becoming a messaging platform.
Native Solution
Sharing must be embedded within Spotify’s core listening flow.
Effortless Action
Sharing must feel immediate and does not interrupt listening.
Focused Scope
Enhances listening without becoming a messaging platform.
WORKSHOPPING SESSION




HMW: How might we enable listeners to share music without adding complexity or disrupting listening?
EXPLORED CONCEPTS
EXPLORED CONCEPTS
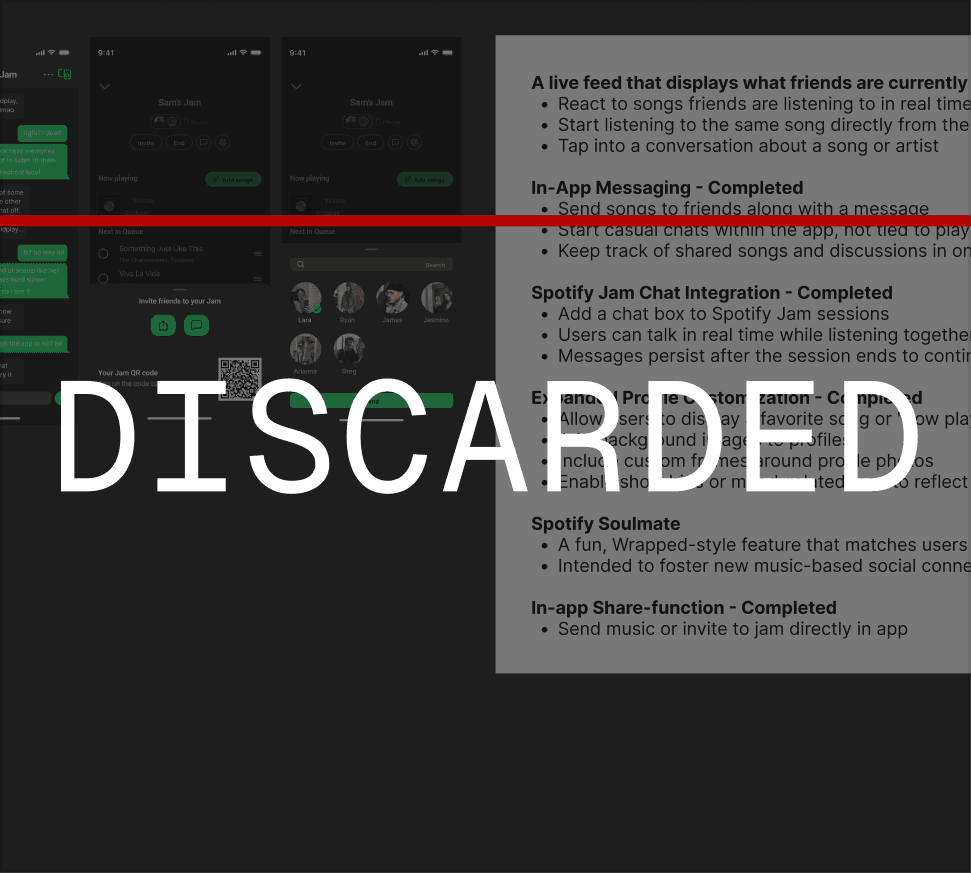
Discarded concept explorations
Discarded concept explorations
Several concepts emerged from the workshop, including persistent messaging layers and dedicated social surfaces. While compelling, they introduced complexity and expanded the product beyond the principles we defined. The following concept illustrates one such direction and why it was ultimately discarded.
Workshops surfaced concepts like persistent messaging and dedicated social layers. While compelling, they expanded scope and were not pursued. One such direction is outlined below.
JAM-SESSION CHAT
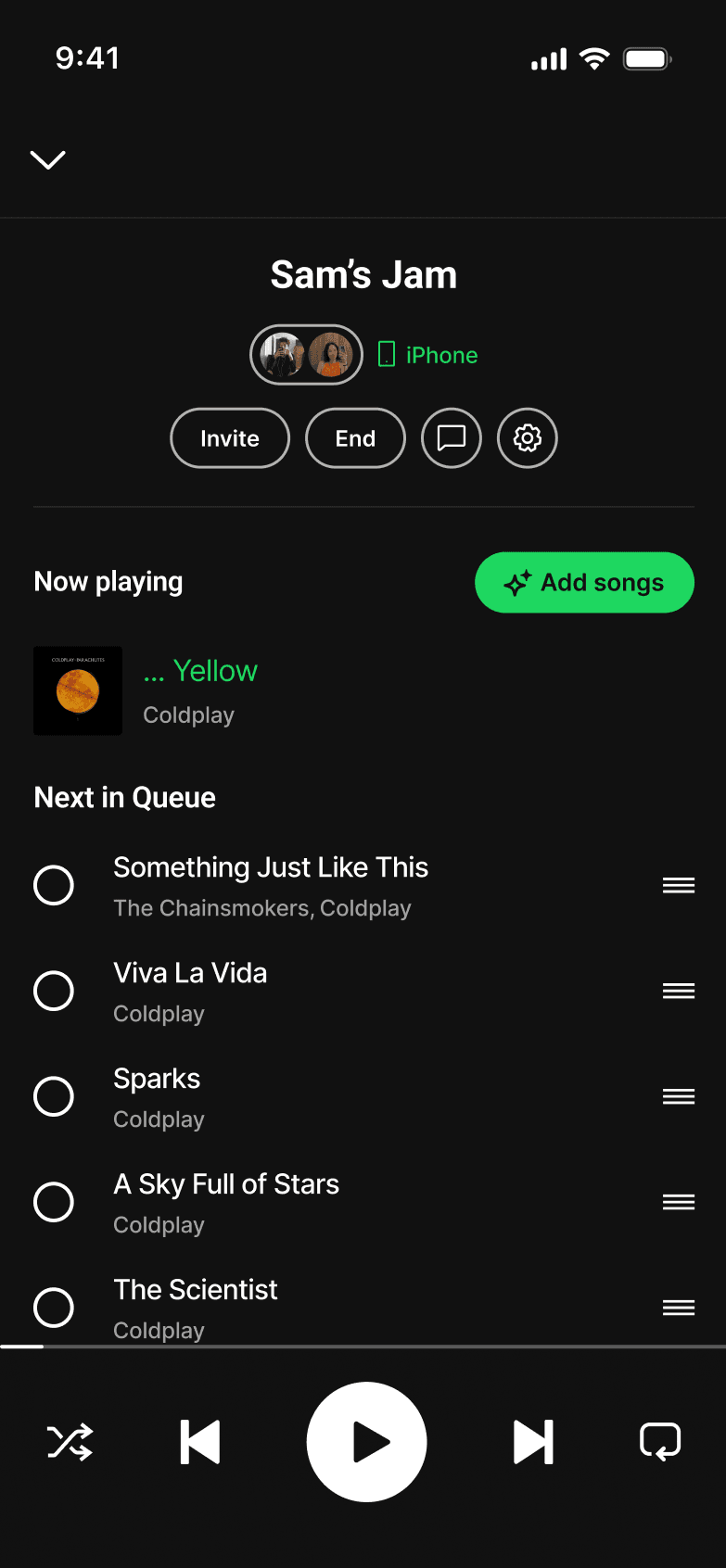
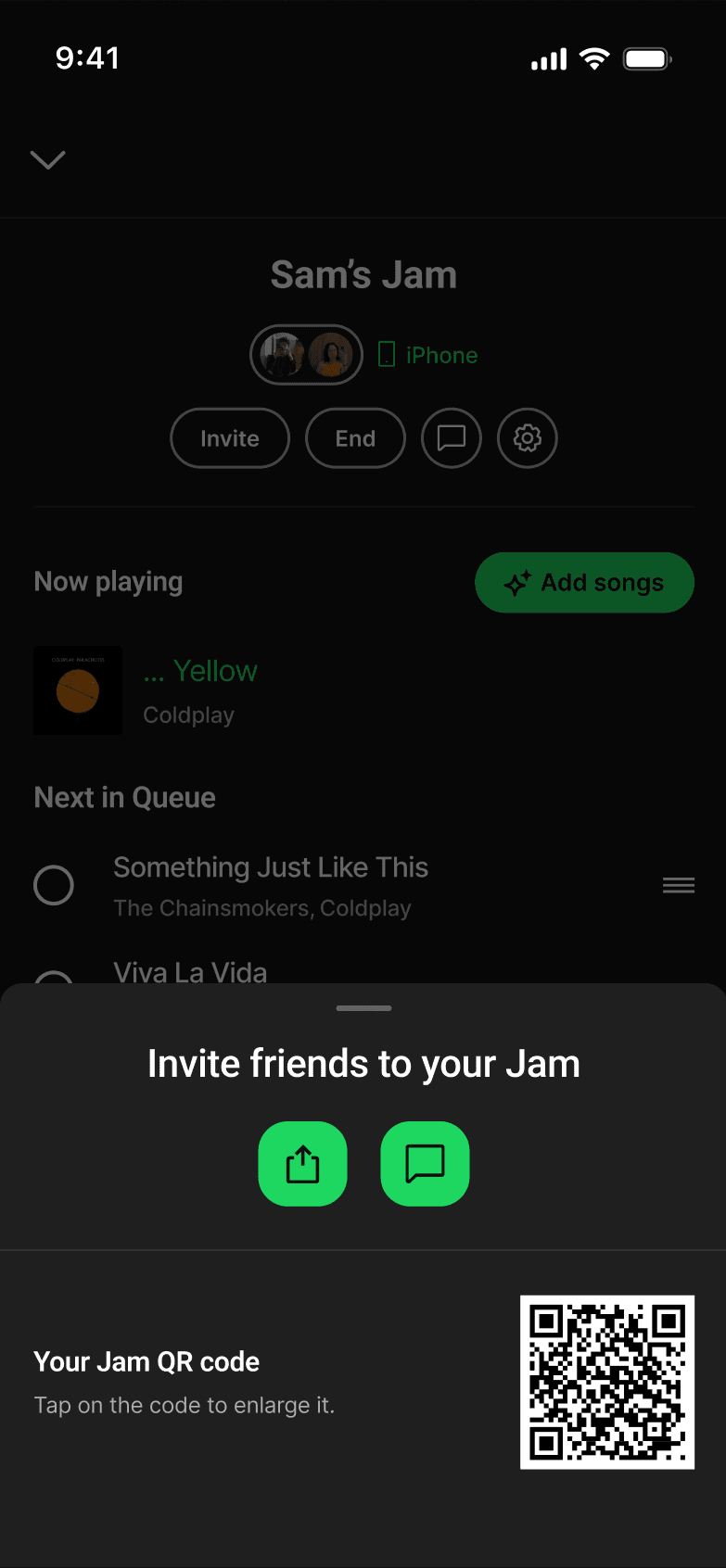
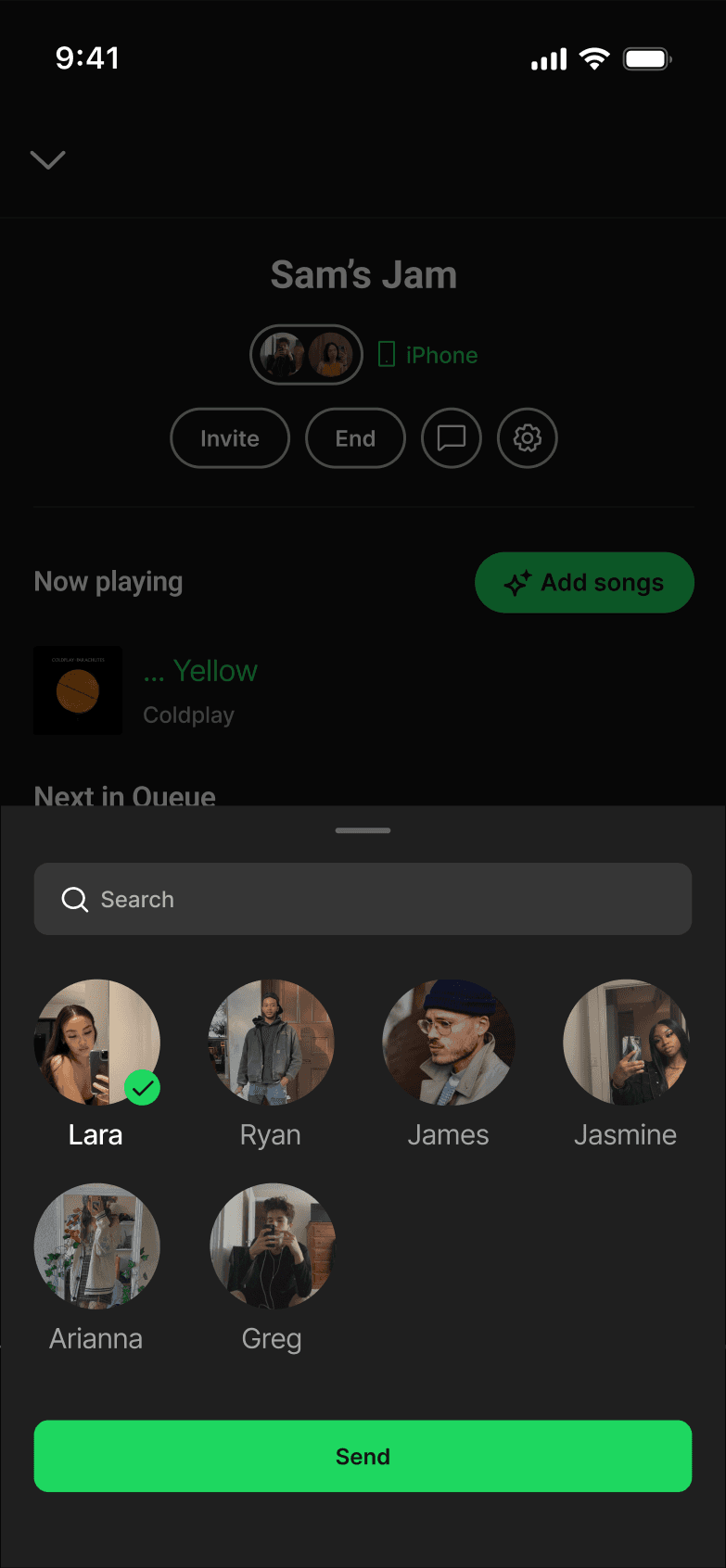
Jam chat introduced messaging within Jam sessions. This violated the Focused Scope principle by shifting Spotify into a messaging app instead of fixing how listeners shared their music.
Testing Approach: I employed task-based usability testing to compare time-to-share and task success against the existing sharing flow and several iterations. Participants were tasked with sharing songs as to measure speed and perceived effort within the moment of intent.
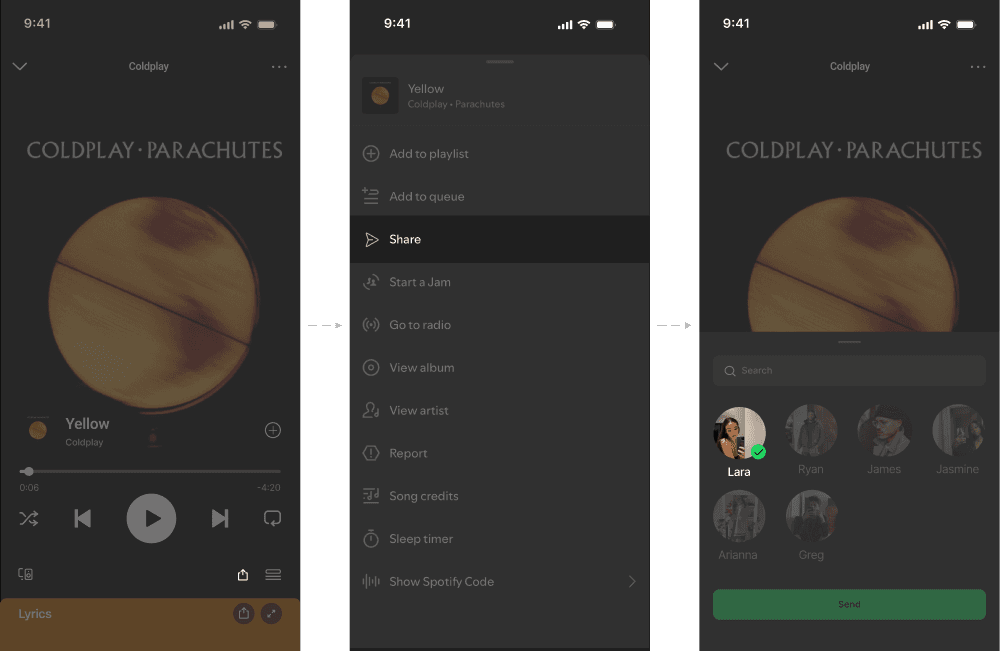
SELECTED SHARE FLOW

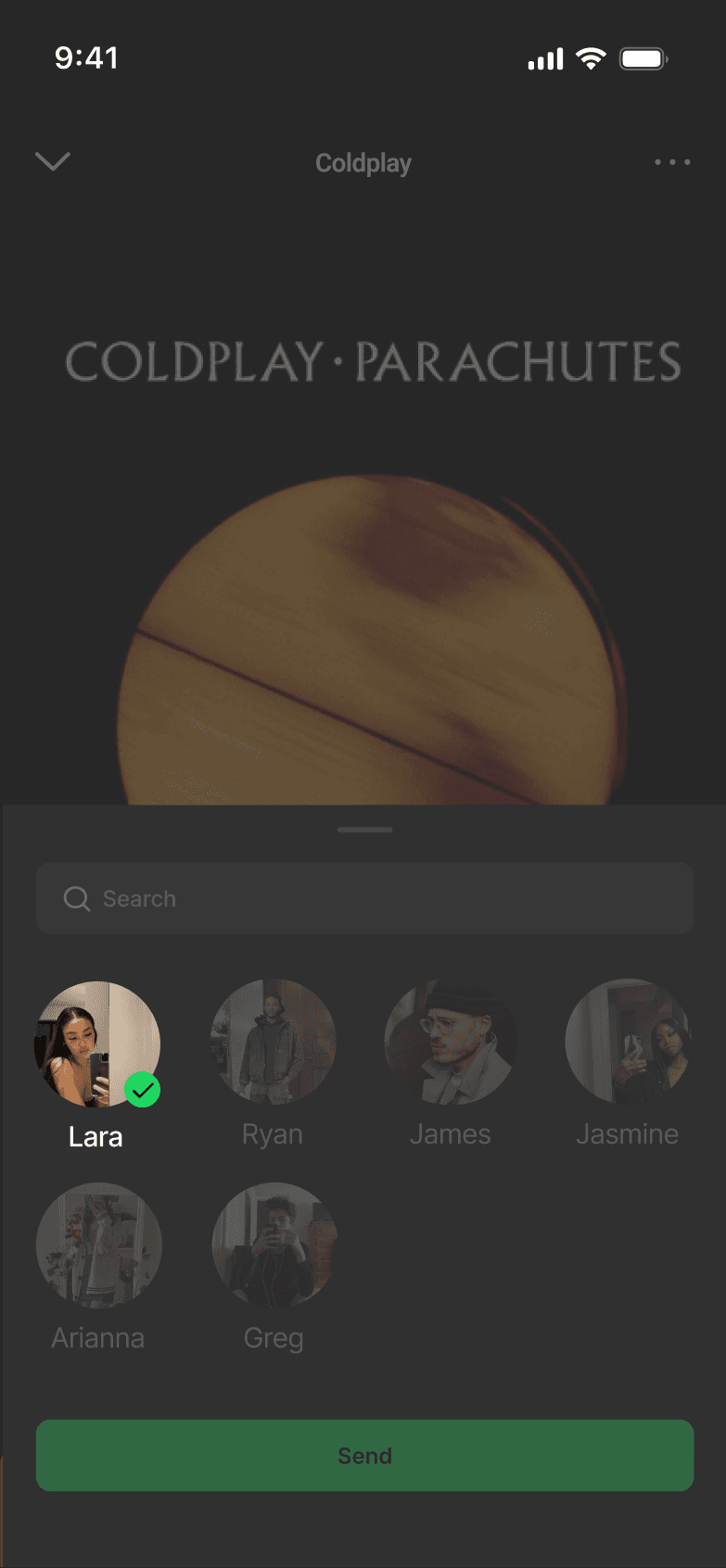

DISCARDED SHARE FLOW
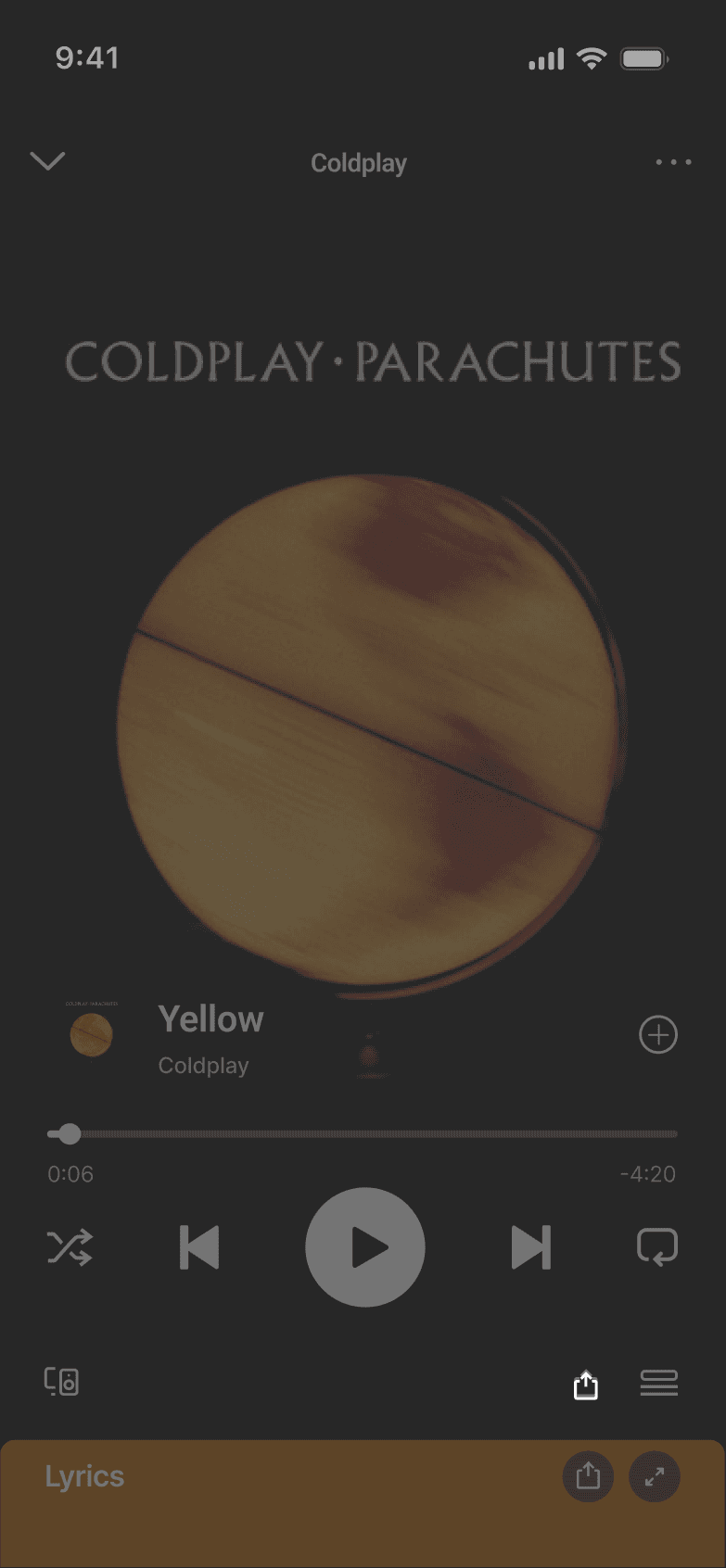
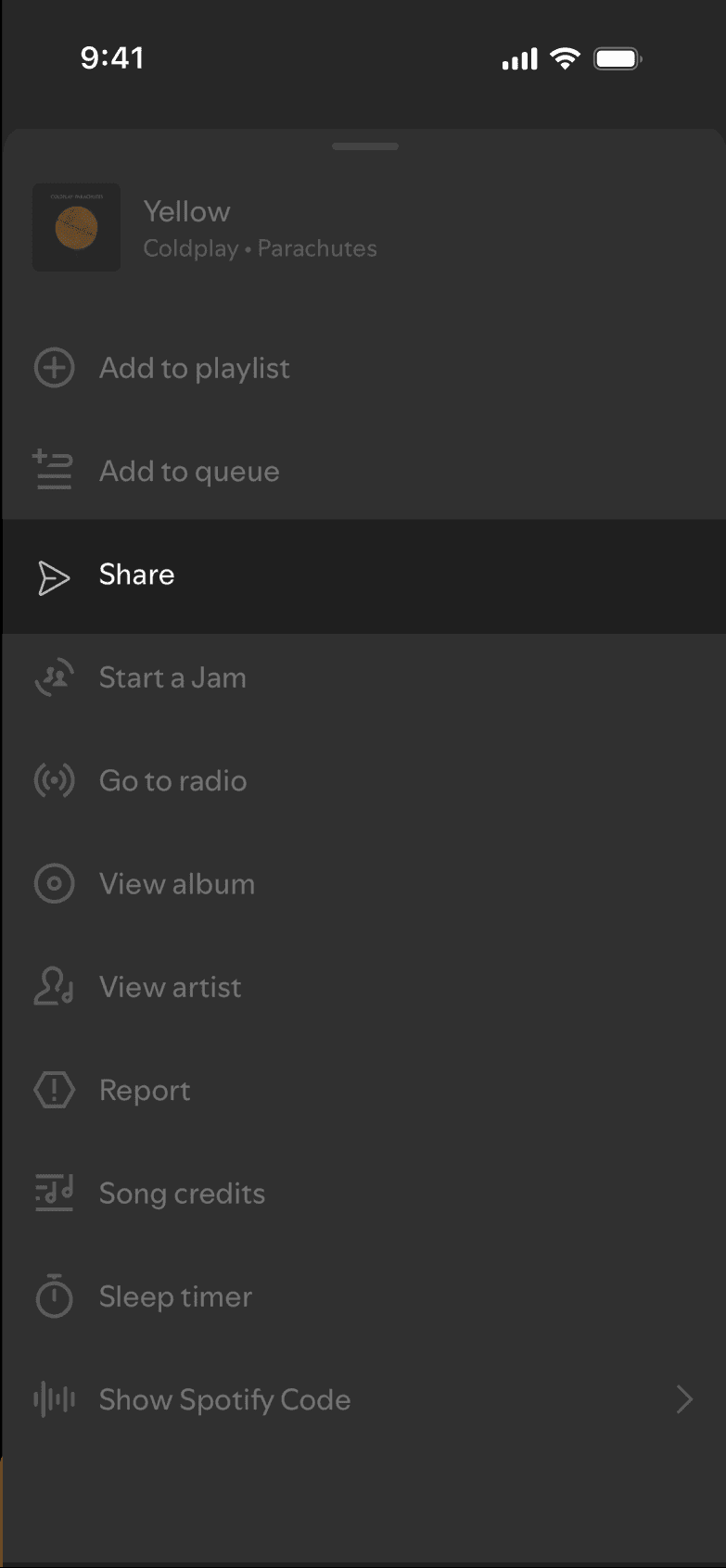
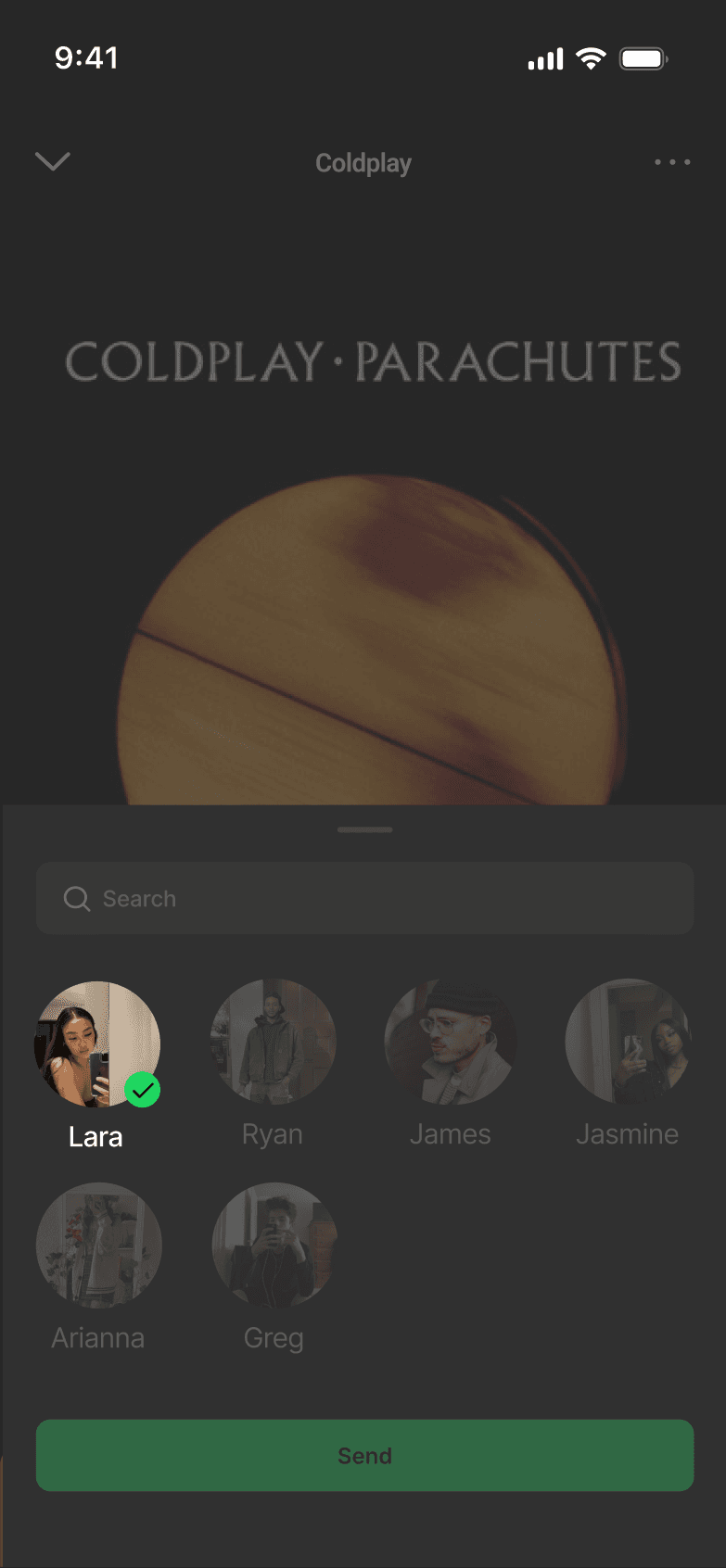
Testing Approach: Task-based usability testing compared time-to-share and task success against the existing flow to validate reduced friction and perceived effort.
JAM-SESSION CHAT
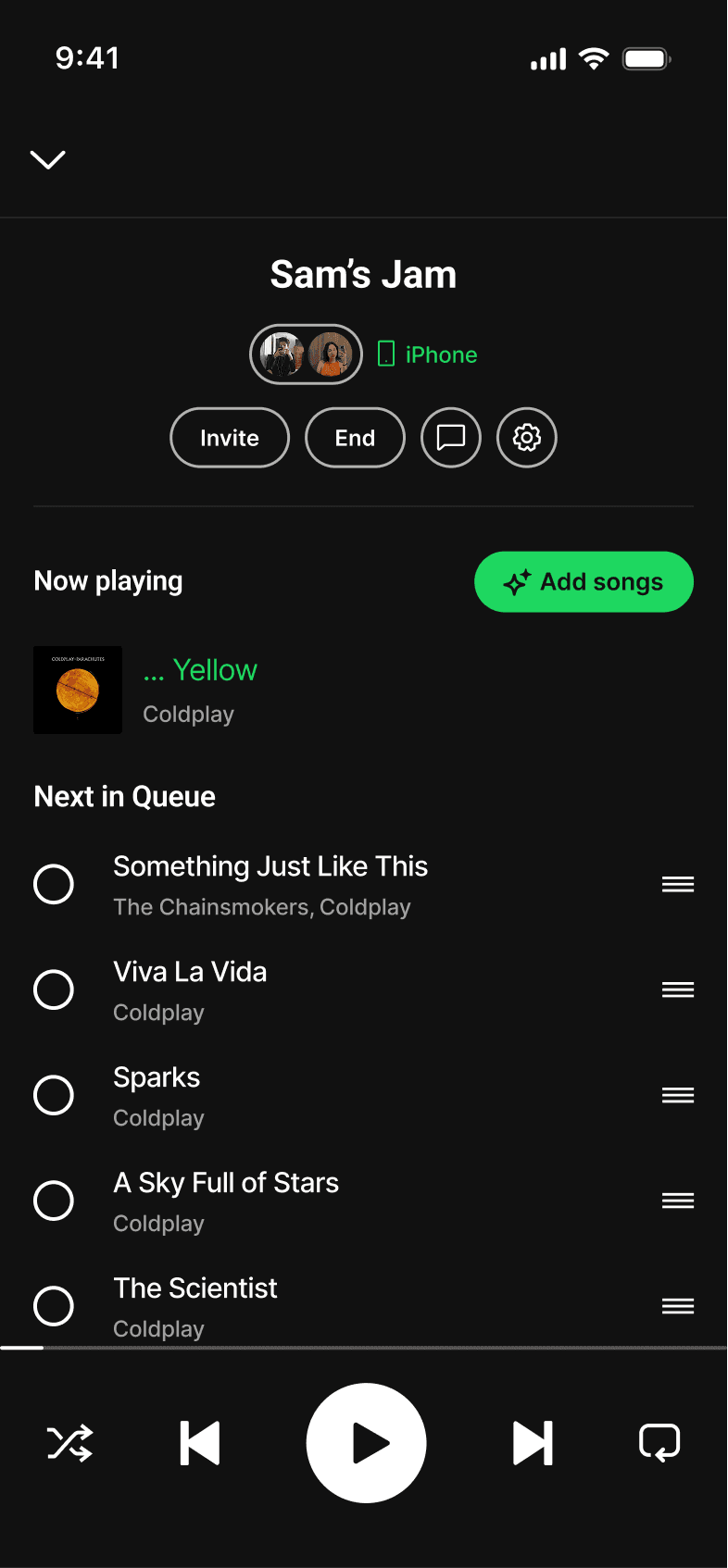

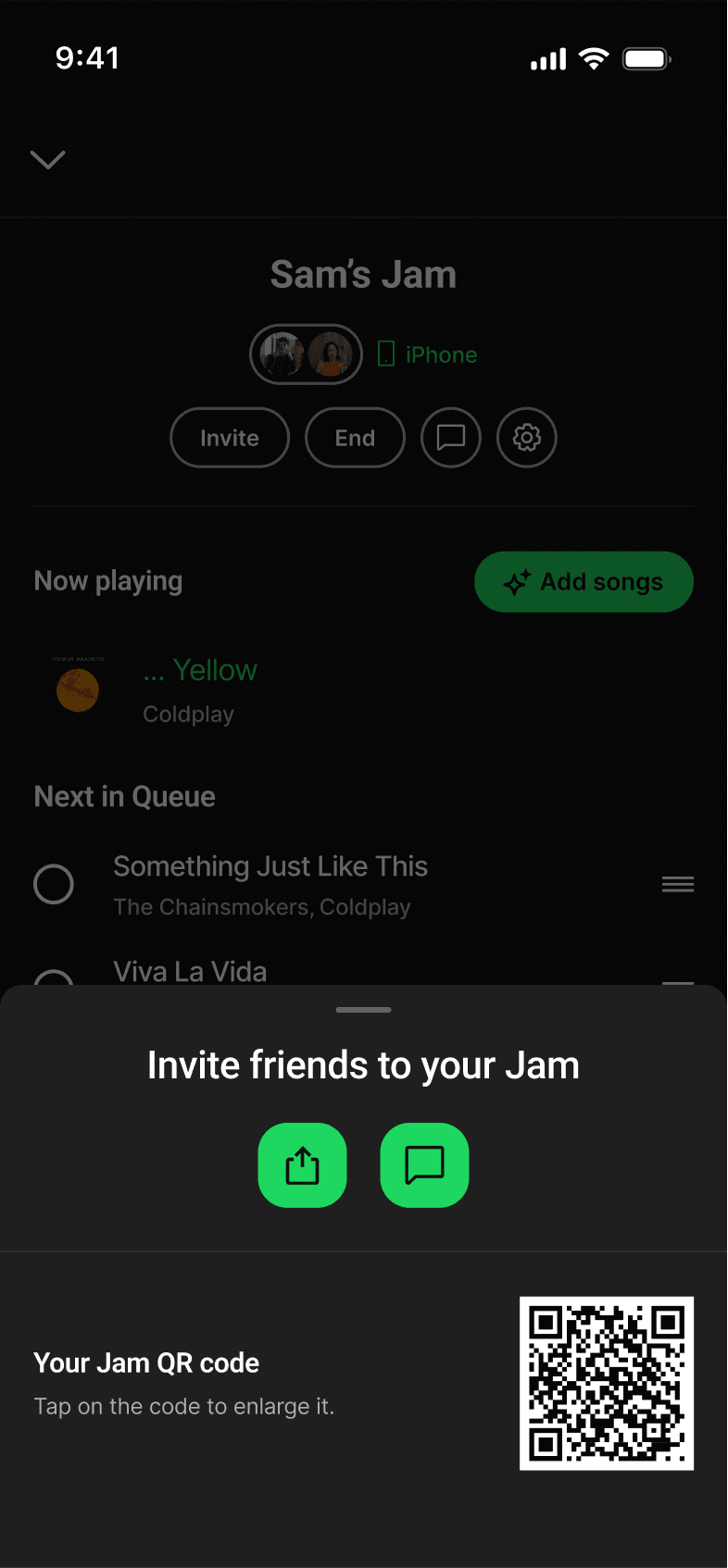

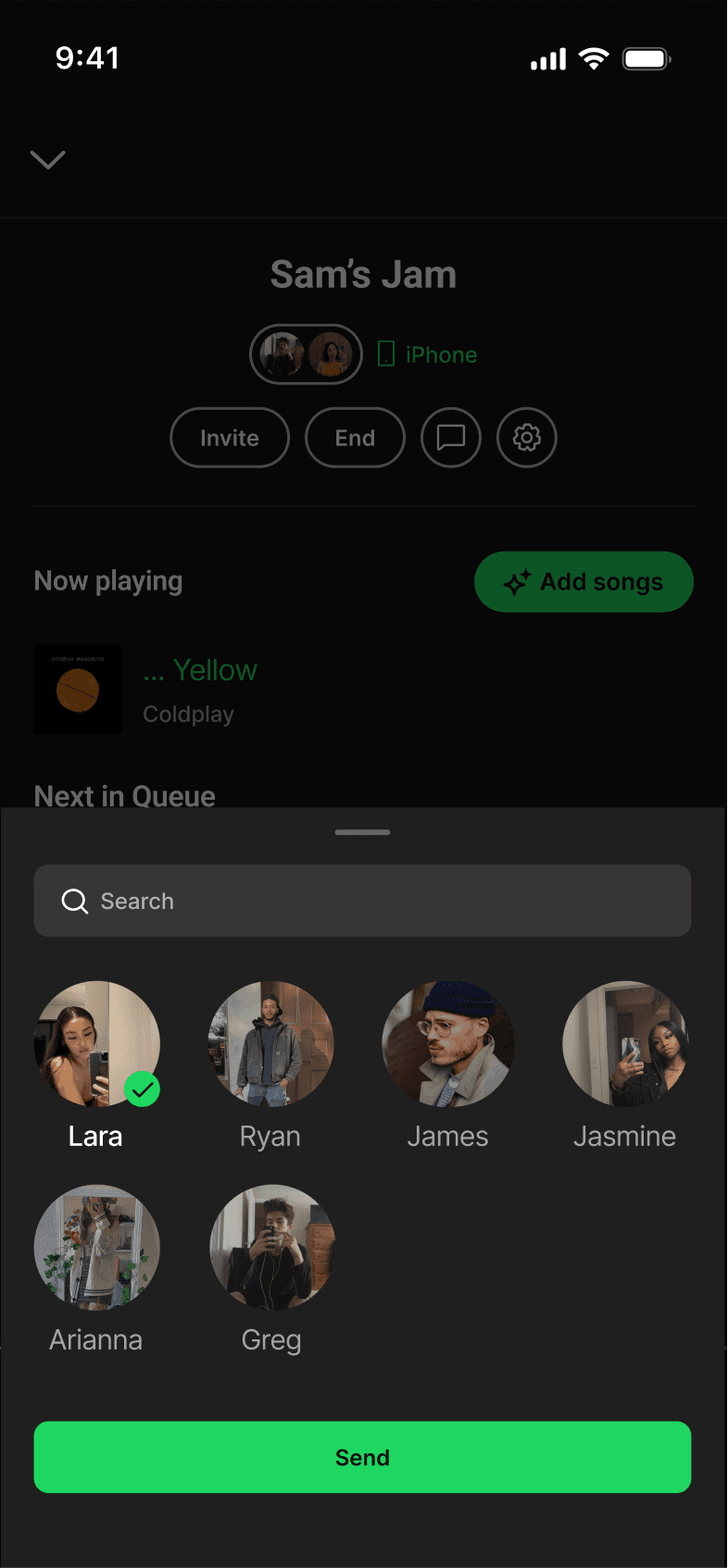

Jam chat introduced messaging within Jam sessions. This violated the Focused Scope principle by shifting Spotify into a messaging app instead of fixing how listeners shared their music.
SELECTED SHARE FLOW
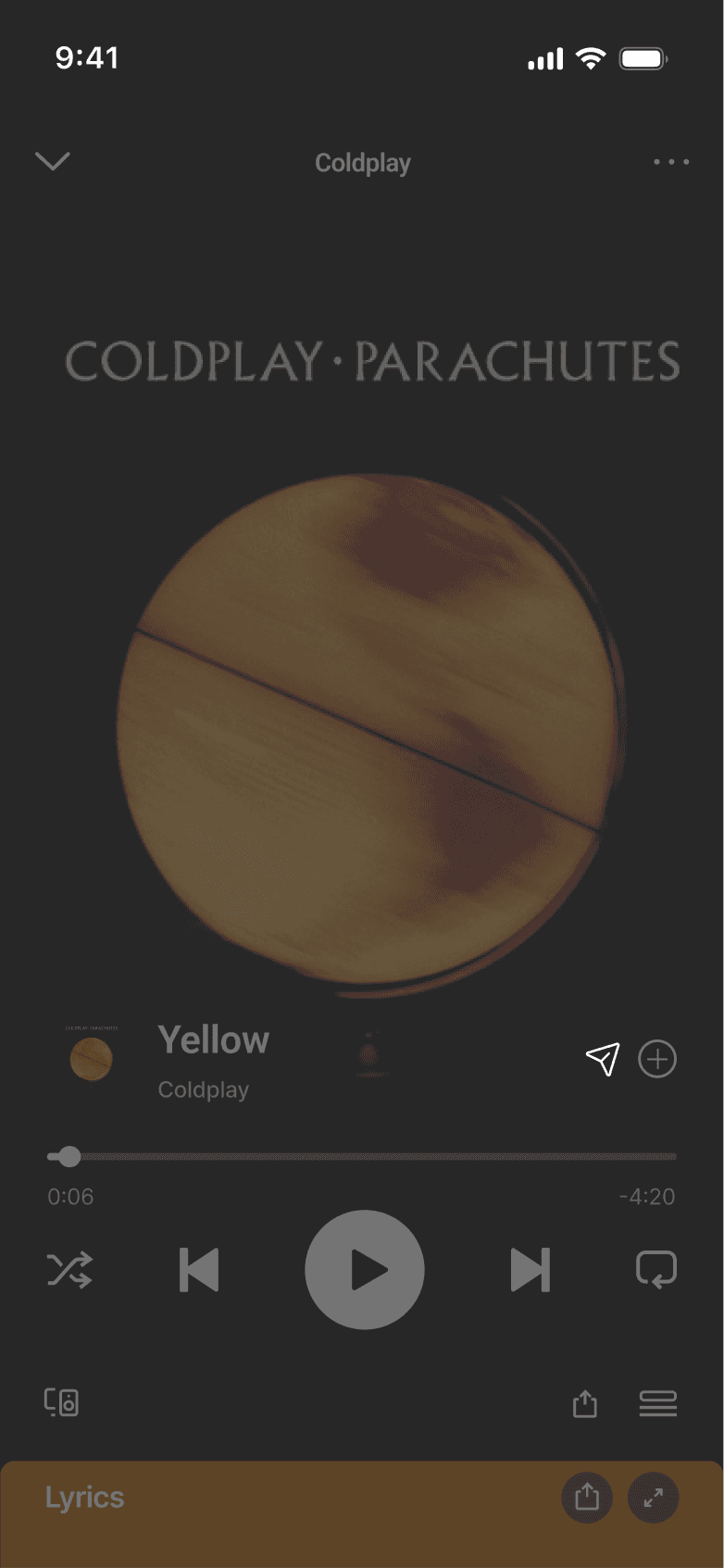

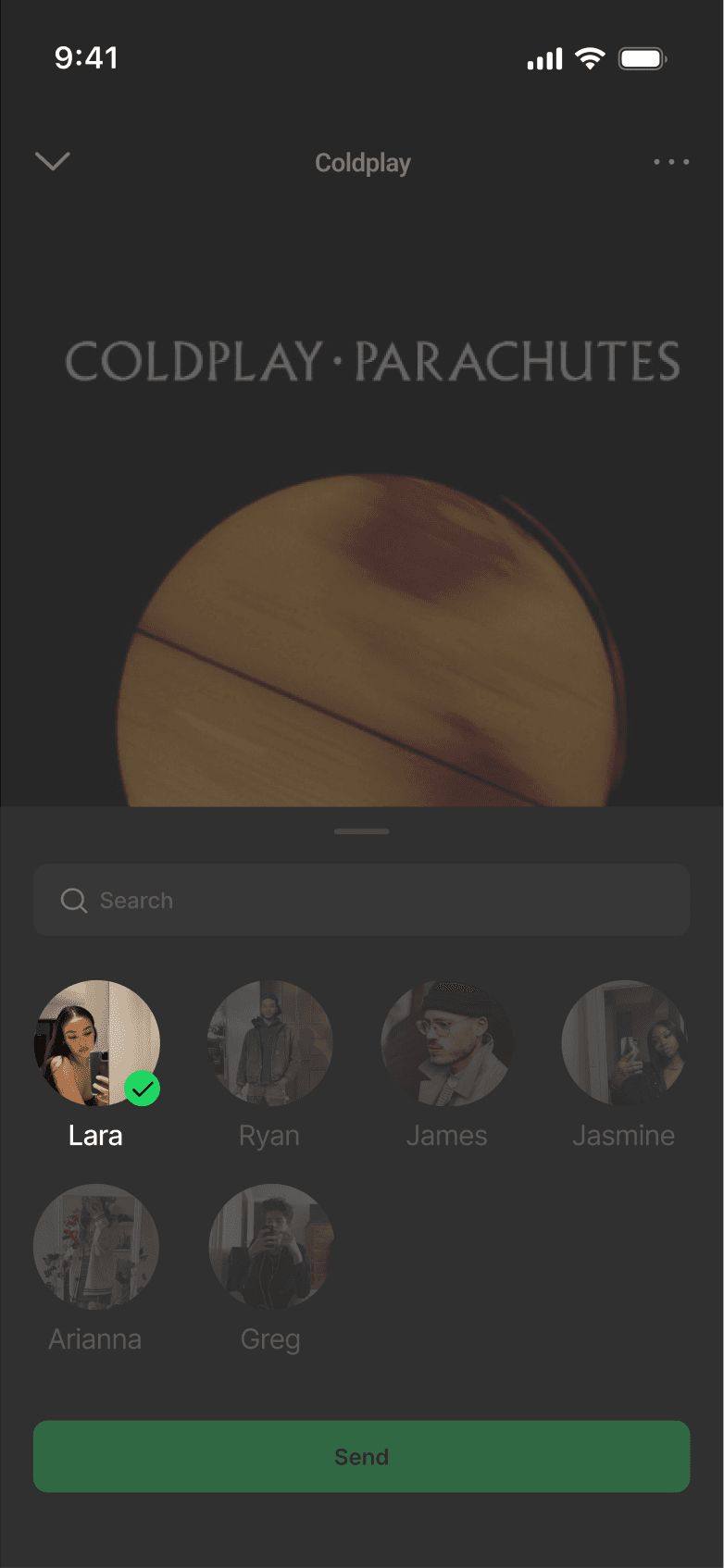

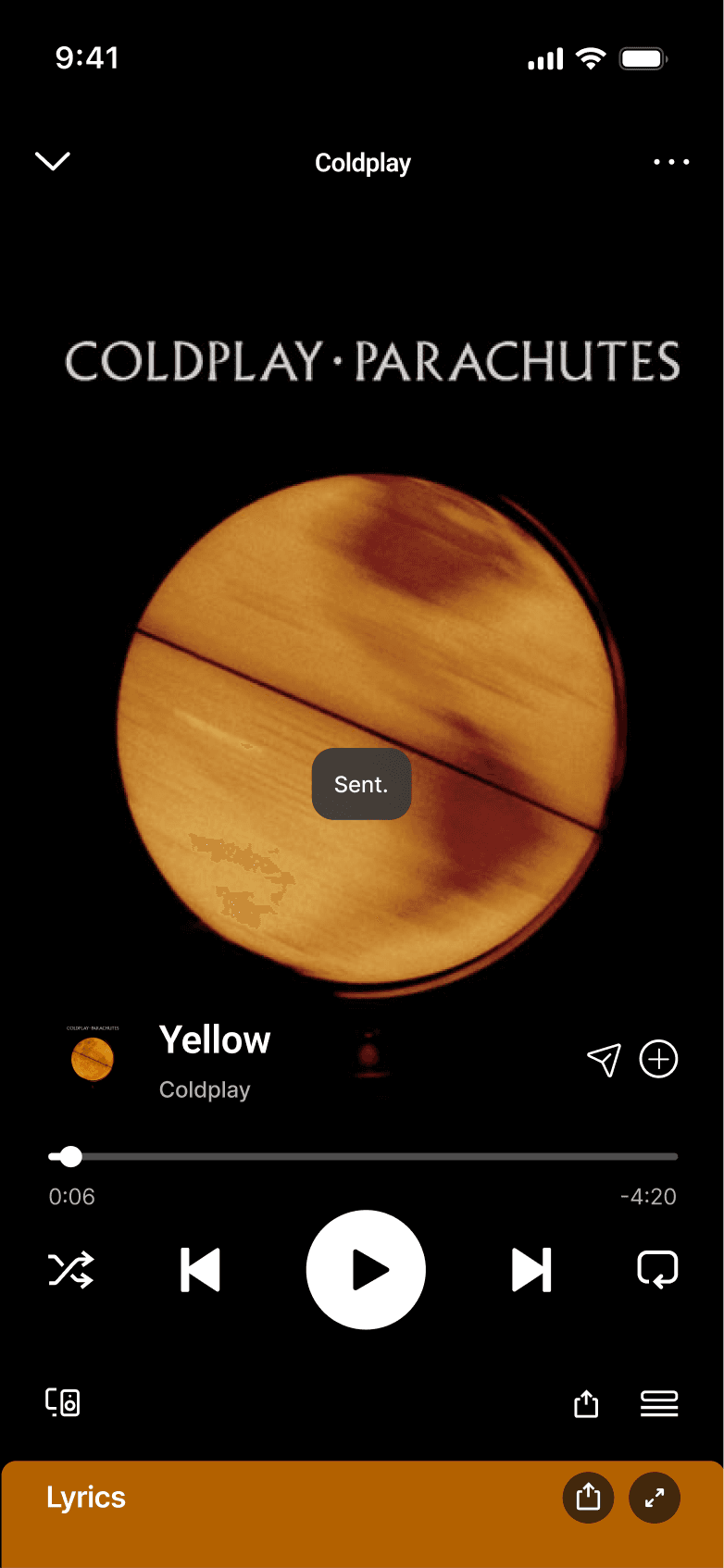

DISCARDED SHARE FLOW
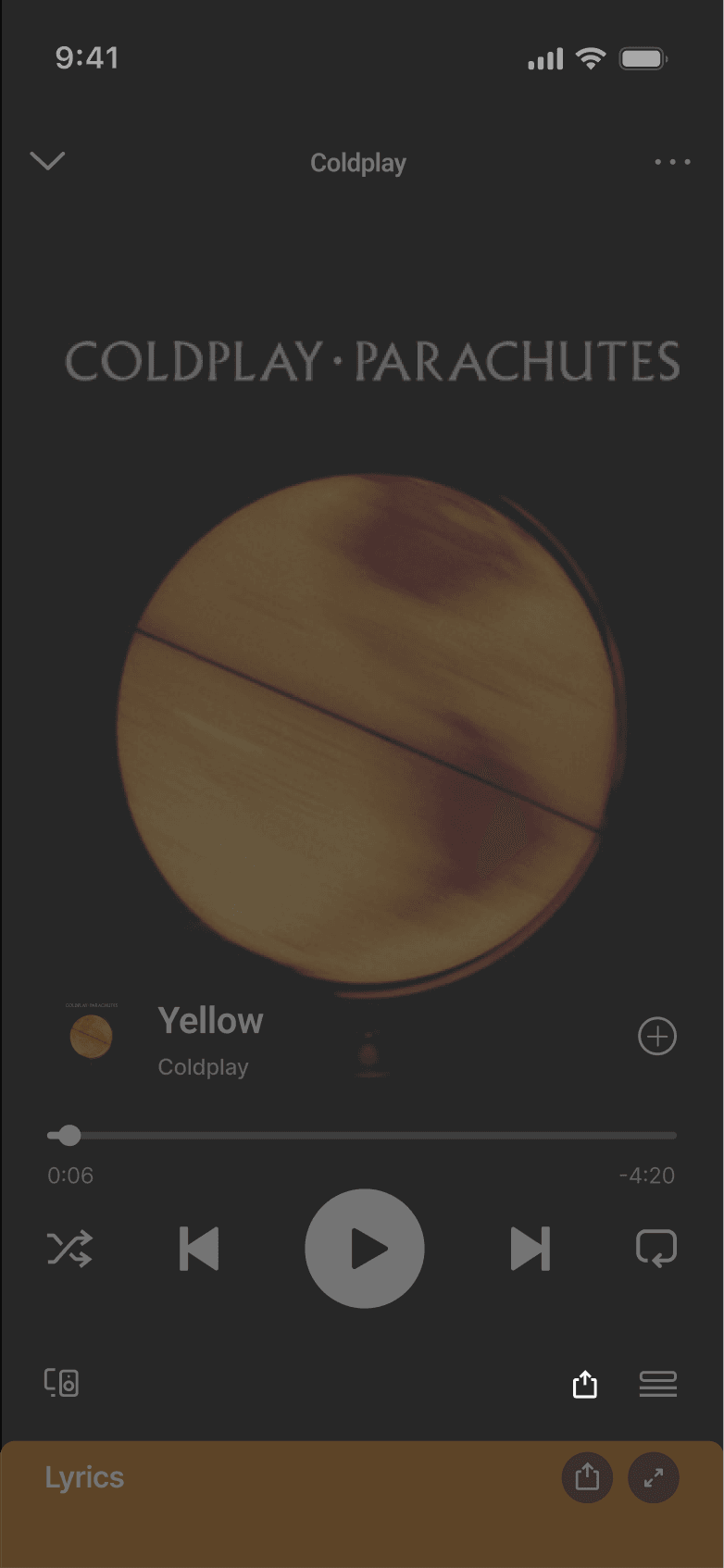

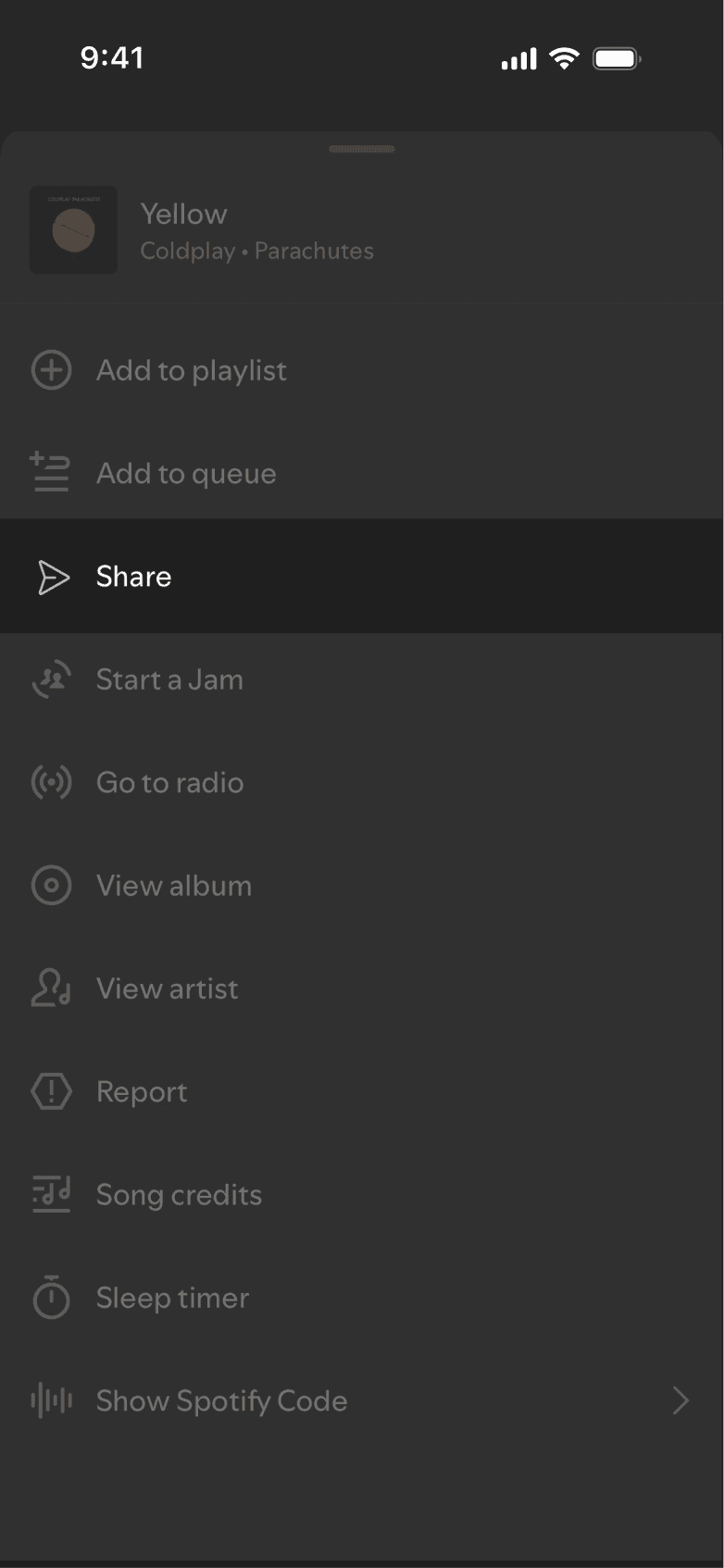

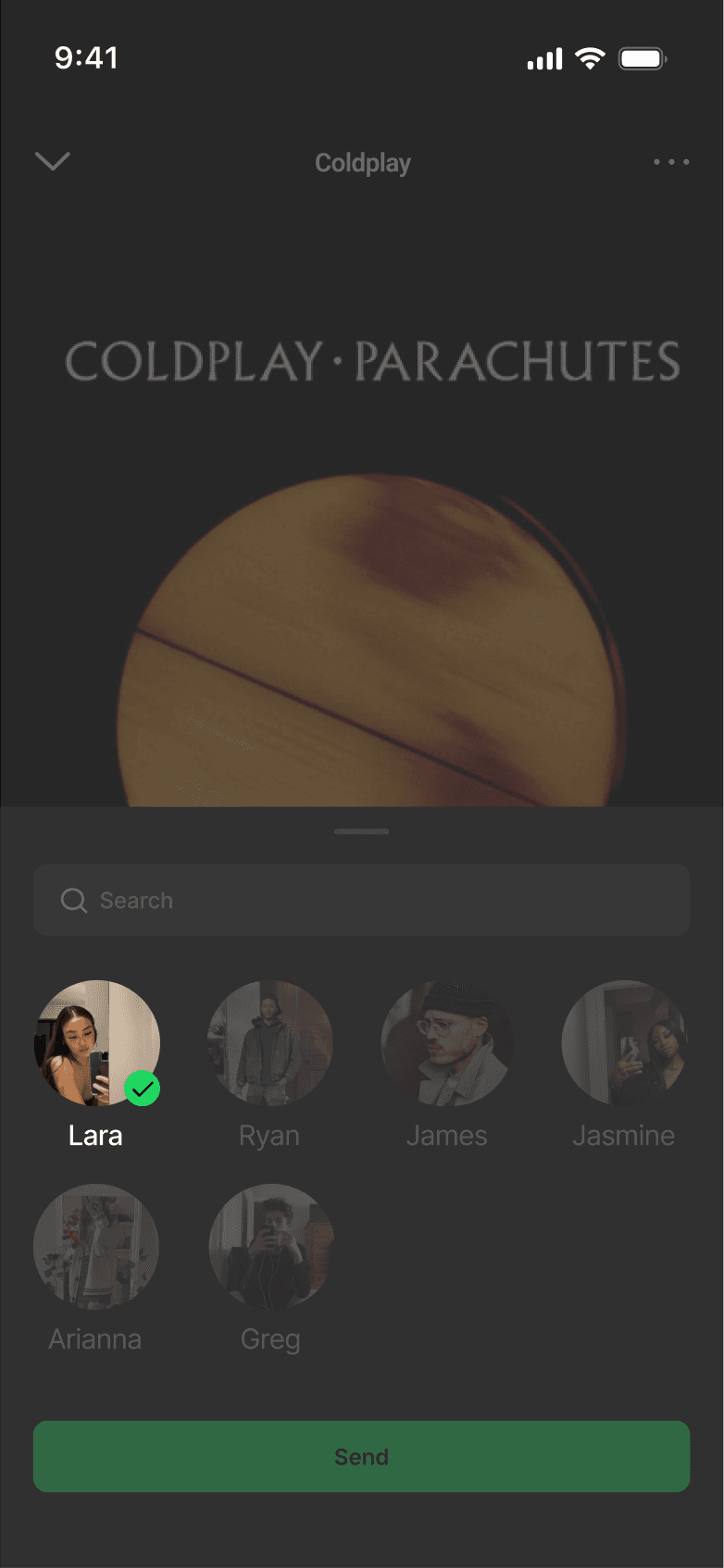

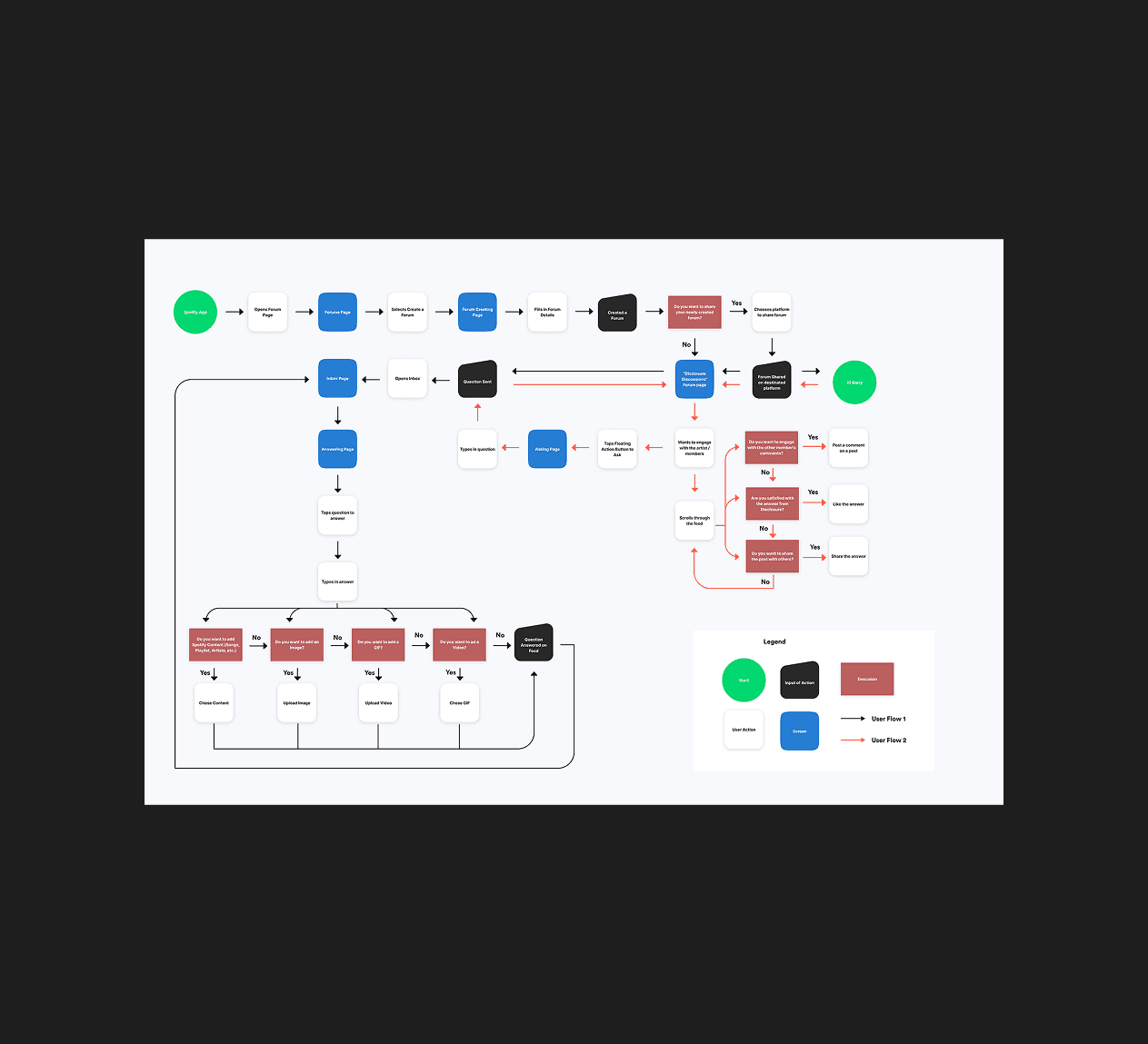
KEY FLOWS
KEY FLOWS
Integrating sharing into core flows
Integrating sharing into core flows
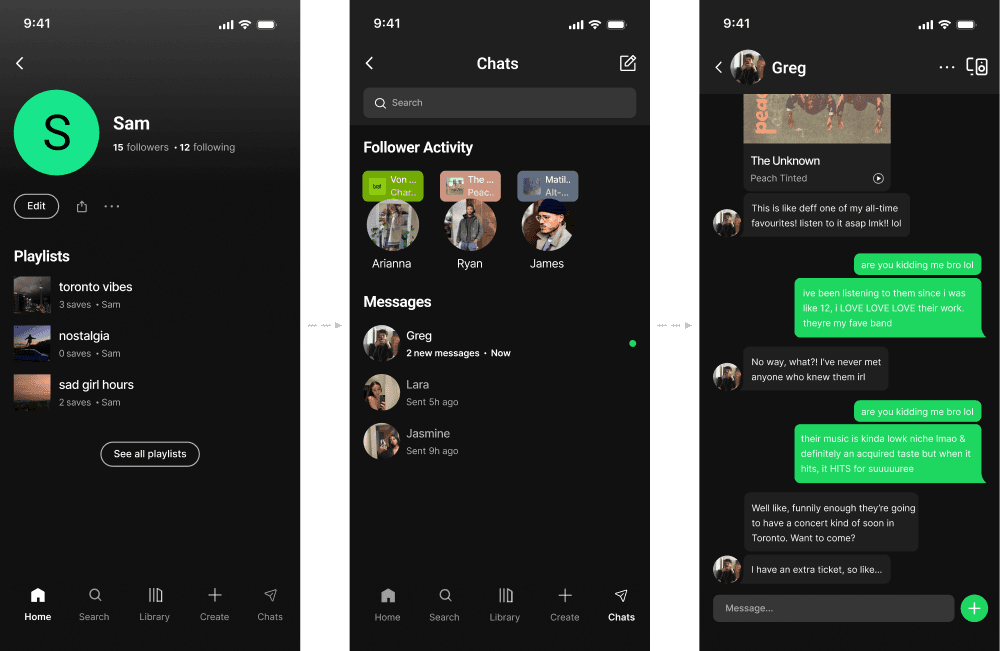
Sharing is now directly embedded within the core listening flow to support in-the-moment interaction. The entry points are positioned at points of intent to enable fast, low-friction music sharing. This shifts the existing music sharing flow from being an export action to an embedded interaction layer.
Sharing is now directly embedded within the core listening flow to enable fast, low-friction interaction. This shifts sharing from an export action to an integrated interaction layer.
QUICK SHARE
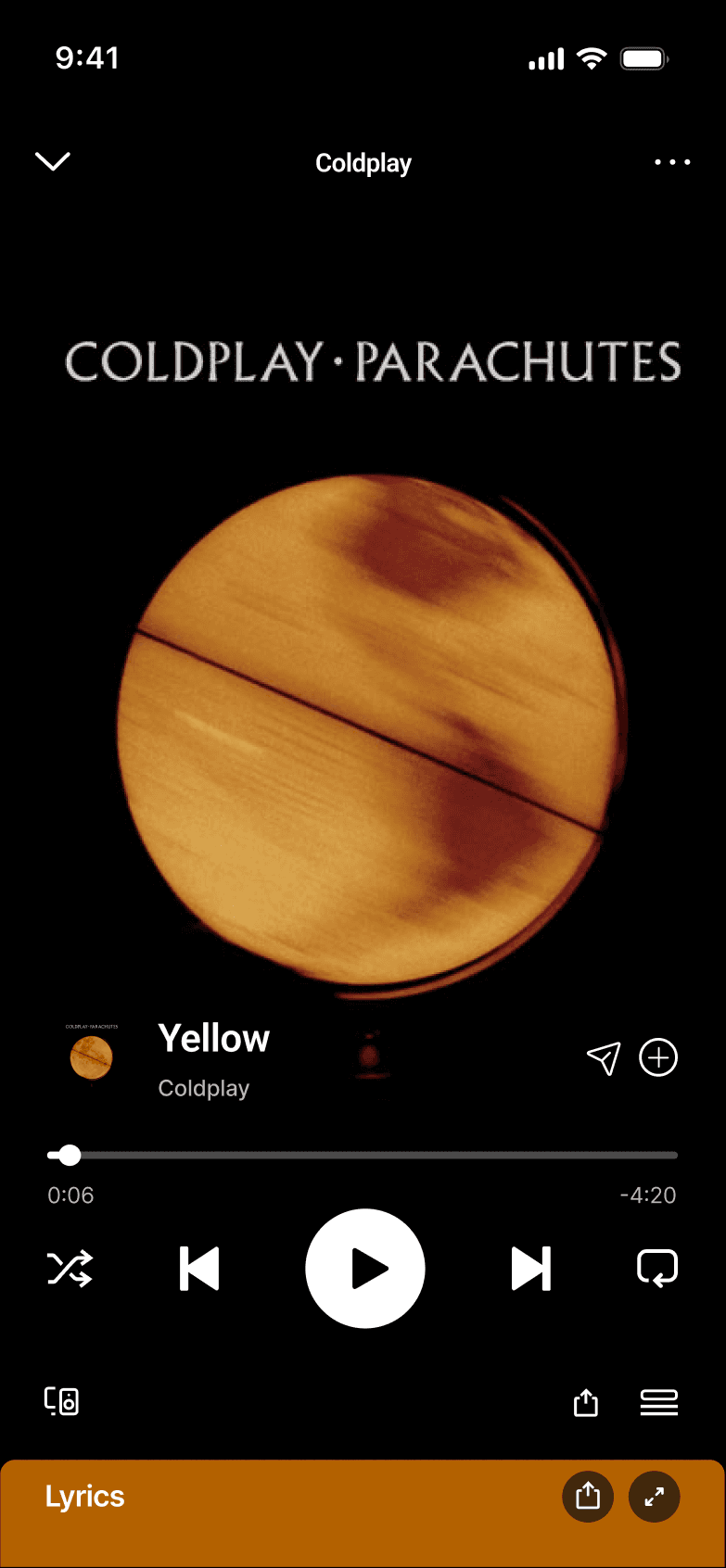


Quick share integrates directly into the player to enable immediate, low-effort sharing. This reinforces Effortless Action by removing cognitive load at the moment of intent.
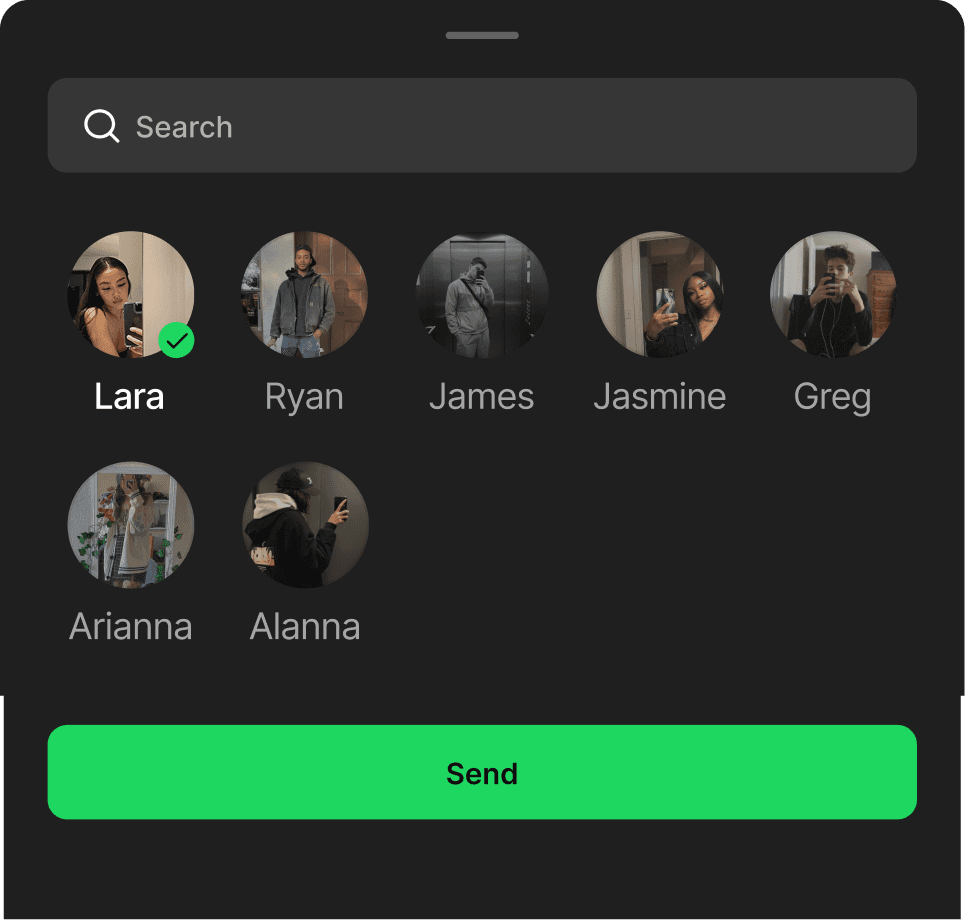
INBOX


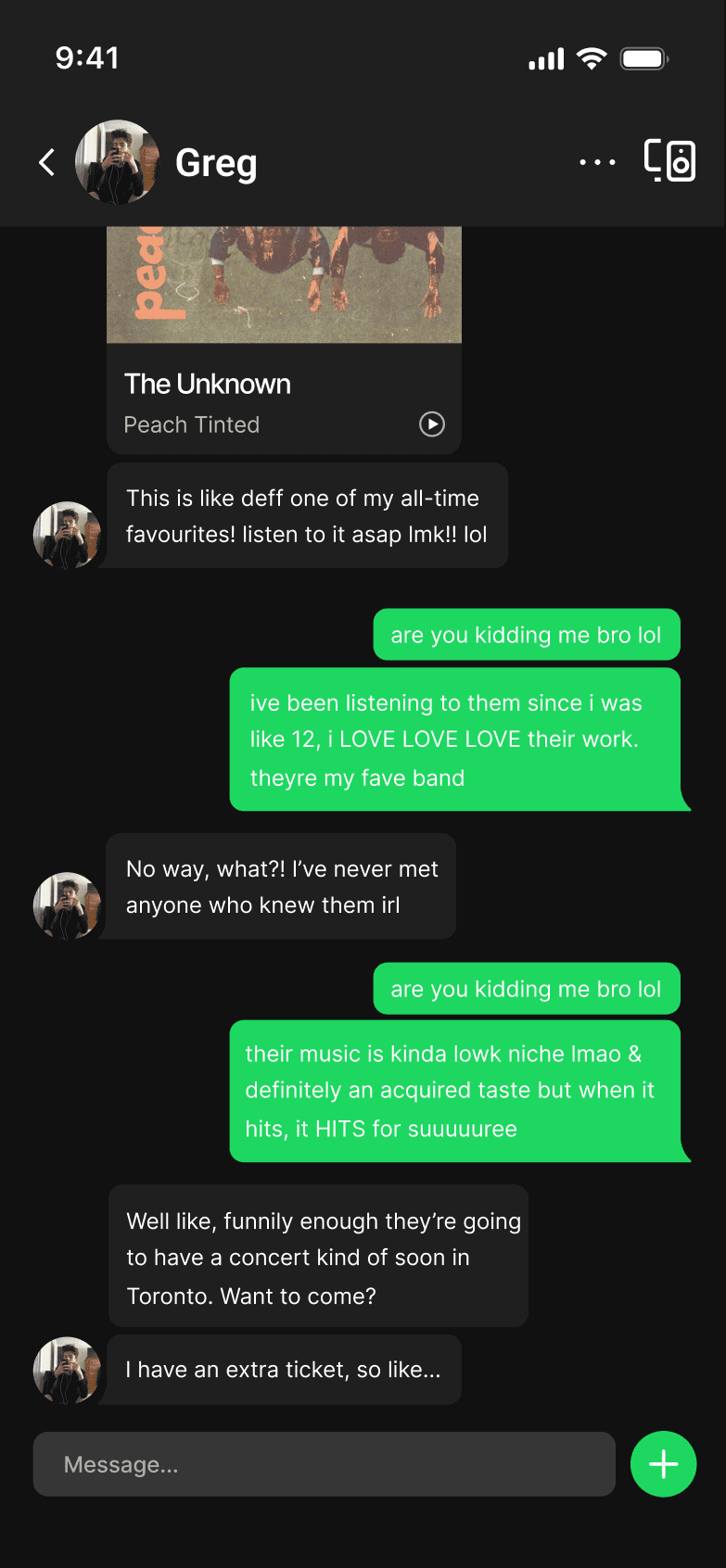
Native inbox creates a dedicated space to share music, add context, and exchange ideas. It keeps interaction centered on the music itself without introducing layered complexity.
QUICK SHARE
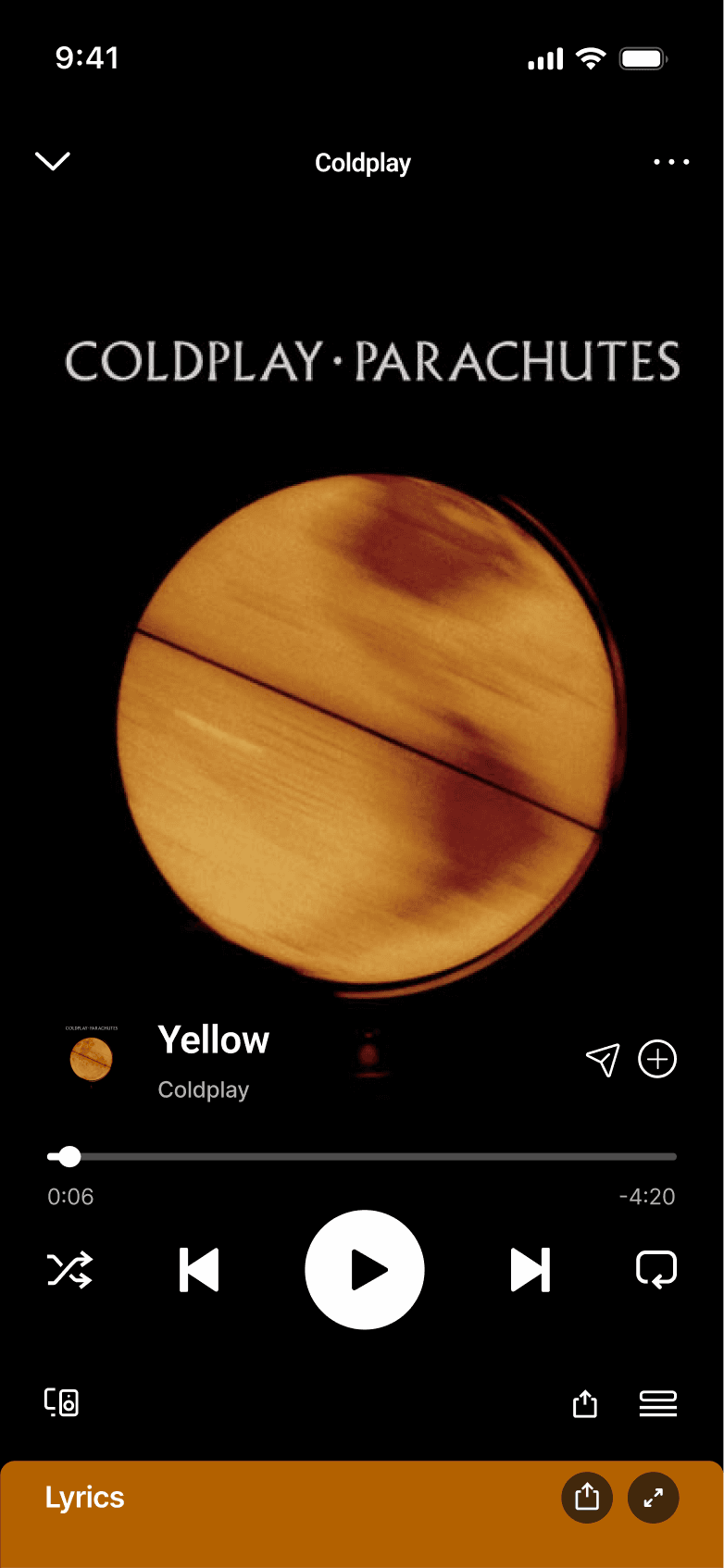

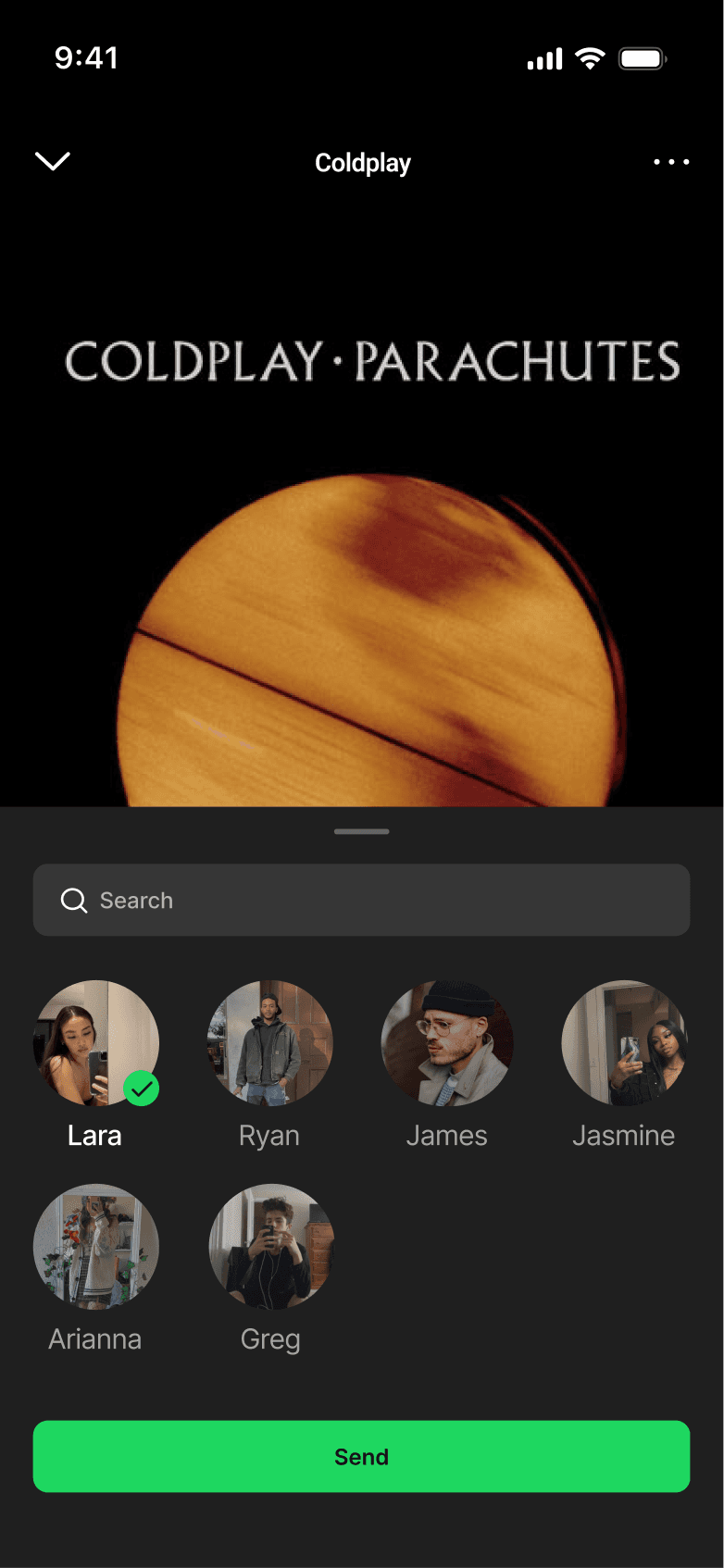



Quick share integrates directly into the player to enable immediate, low-effort sharing. This removes cognitive load at the moment of intent.
INBOX
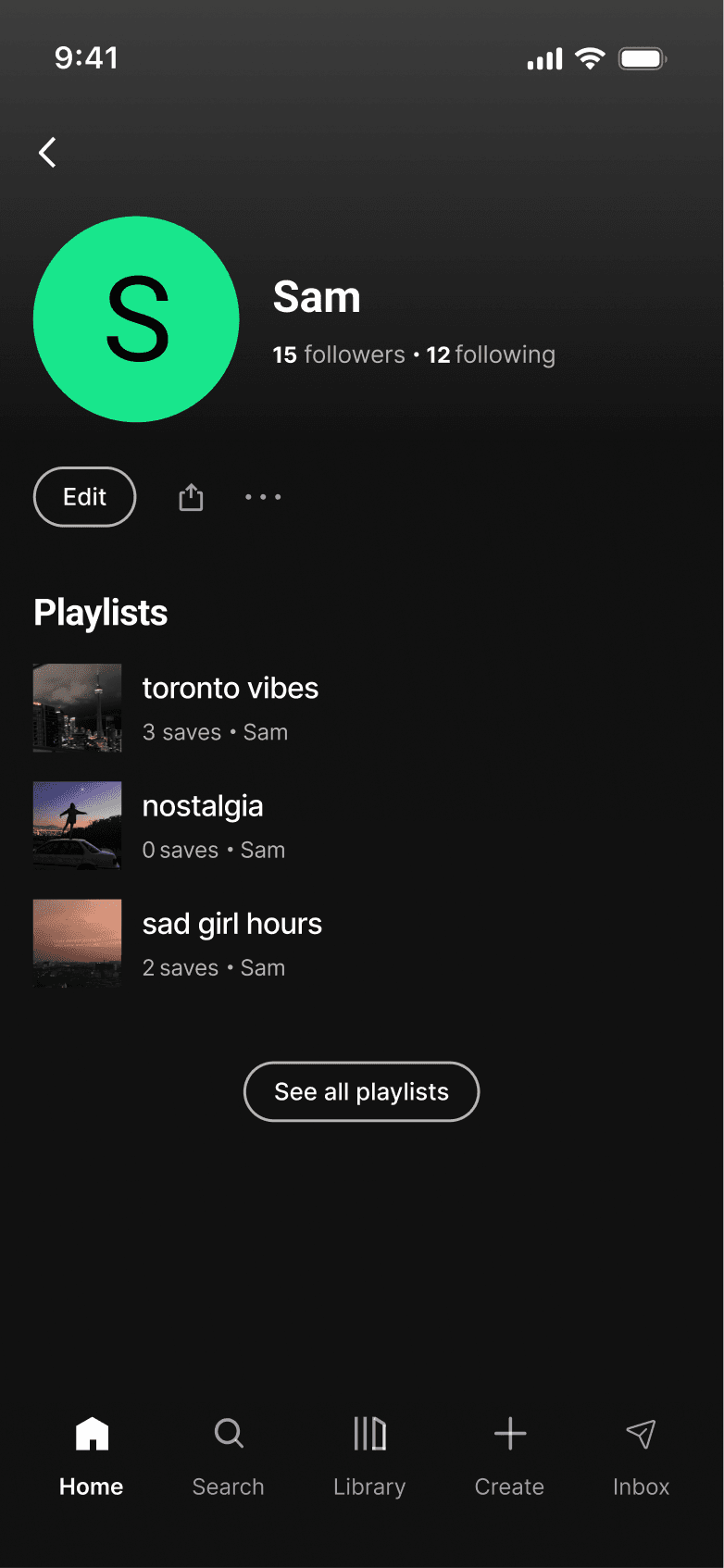

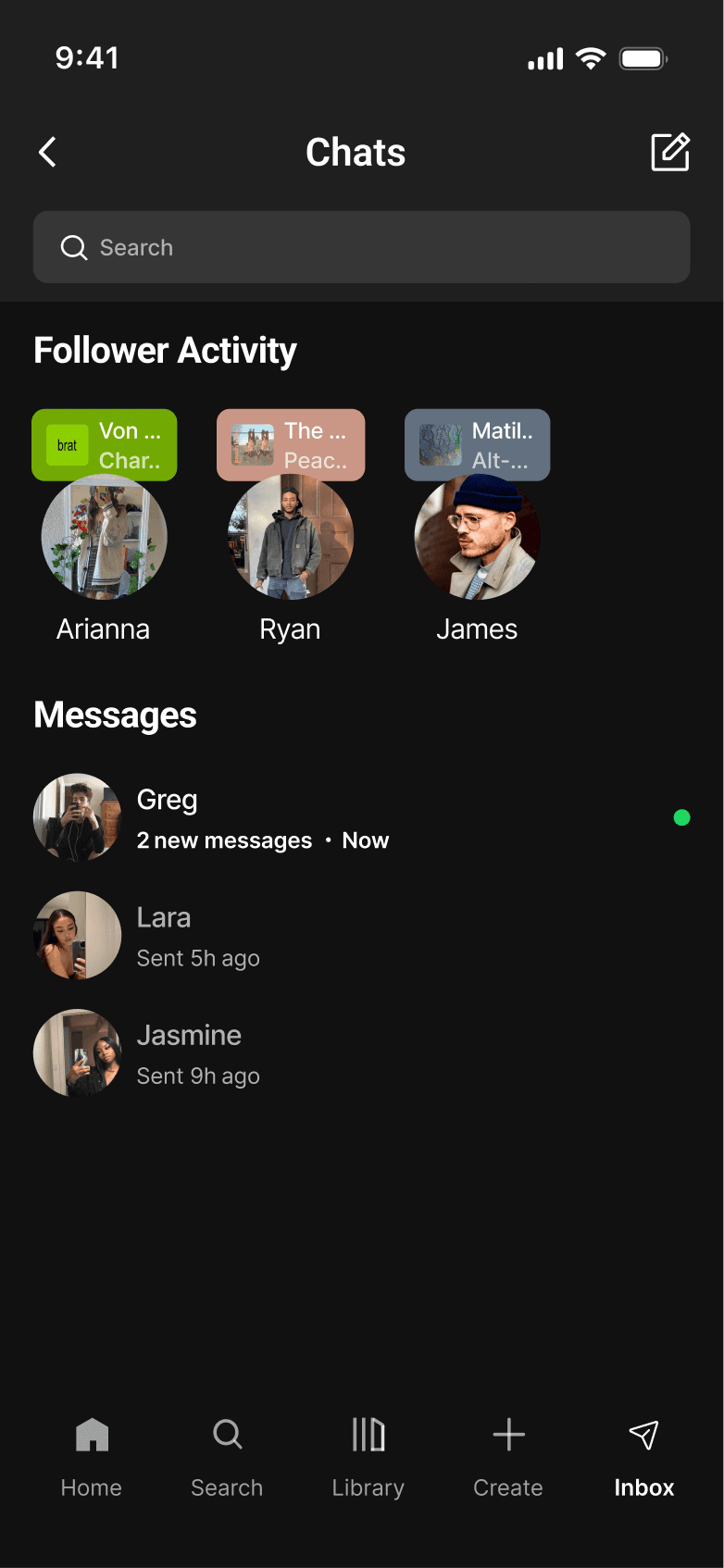

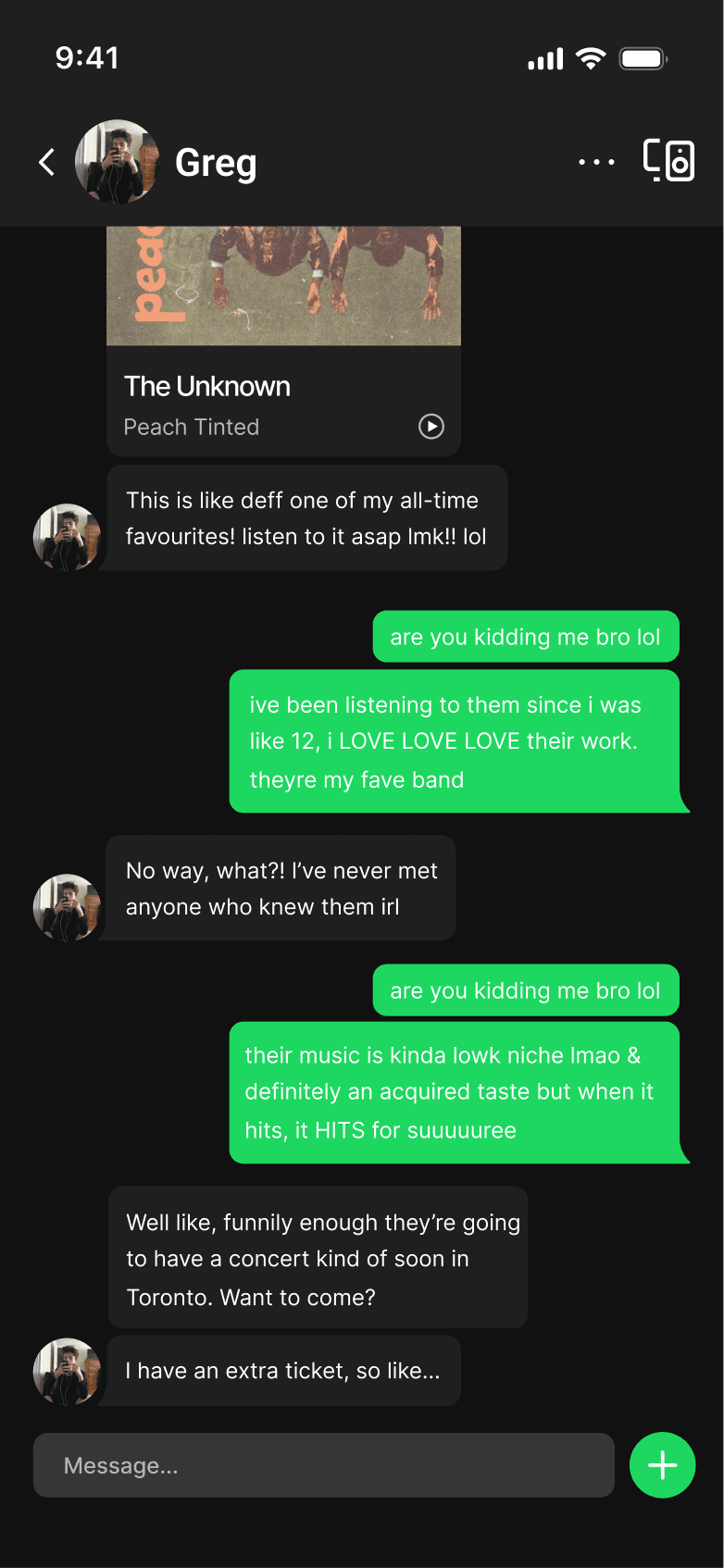

A native inbox creates a dedicated space for users to share music. It keeps interaction centered on music without introducing more complexity.
REFLECTION
REFLECTION
Solving the right problem
Solving the right problem
This project reinforced the importance of solving the right layer of the problem. Although research pointed toward listeners wanting deeper social features, the core issue was friction around sharing. Expanding into messaging would have increased scope without addressing that structural breakdown. By embedding sharing into existing flows, the solution resolved intent while preserving product focus.
This project reinforced solving the right layer of the problem. Sharing friction, not missing social features, was the core issue. Embedding sharing into existing flows resolved intent without expanding scope.
DISCARDED CONCEPTS
DISCARDED CONCEPTS


CONCEPT
2025
Integrated
native music sharing
MOBILE APP
END TO END
B2C


Role
Lead Designer
Team
1 Designer
Timeline
January – February 2025
Skills
UX Design, Research
CONTEXT
External sharing disrupted listening
Spotify relies on external links or third-party apps for sharing. This creates friction in what should be a seamless listening behavior.
Note: Spotify introduced similar native sharing features in May 2025, validating the direction explored in this case study.
IMPACT
Streamlined music sharing experience
Introducing in-app sharing removes the need to leave Spotify and reduces friction in the sharing process. The simplified flow makes music easier to share in the moment and supports higher engagement around shared content.
OUTCOME
Faster Sharing
when sharing a song in testing.
of User Testing Participants
when completing sharing steps.
Higher Intent
when using native sharing feature.
QUICK SHARE
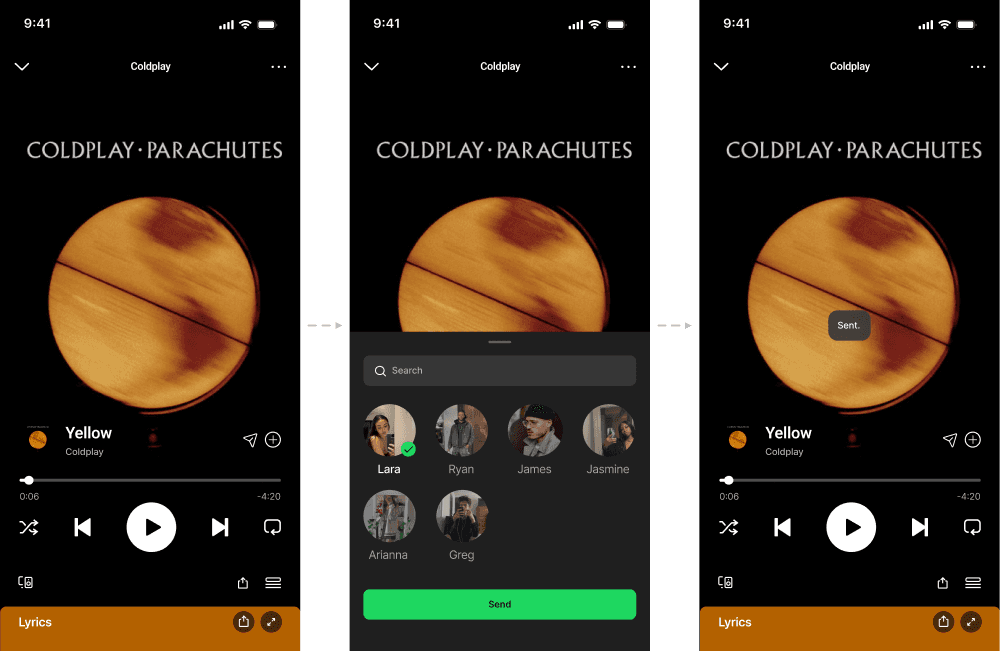

INBOX

PROBLEM DEFINITION
Core sharing flow breaks engagement
Despite new social features, sharing music on Spotify still requires leaving the app. This adds friction to a core behavior and limits engagement around music.
Hypothesis: Increasing intent and accountability would improve follow-through and retention.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
How do Spotify listeners currently share music?
Sharing & Behavior
What issues prevent more frequent music sharing?
Pain Points & Barriers
Do these issues impact app social engagement?
Engagement & Interaction
OBSERVING USERS
Examining real-time sharing behavior
I observed twelve active users sharing music within real listening routines. This exposed consistent breakdowns where the flow diverged from natural behavior.
CONTEXTUAL INQUIRY


KEY PAIN-POINTS
Broken Flow
External sharing adds unnecessary steps that interrupt listening and overall experience.
Cognitive Overload
Leaving the app to share music breaks context and intent, thus weakening engagement with content.
Discouraged Sharing
Higher friction adds to hesitation at the point of sharing, making repeat sharing more unlikely.
UNDERSTANDING USERS
Understanding friction through interviews
I conducted interviews with the same users to understand motivations behind sharing. This phase focused on why users share and what they expect from the interaction.
INSIGHTS
Social Interaction
Users often share music to start social interactions.
Discovery Catalyst
Shared music drives discovery beyond app recommendations.
Trusted Curation
Friends’ recommendations carry more weight than algorithms.
USER SURVEY




COMPETITOR ANALYSIS
Examining competitive interaction models
I analyzed Apple Music and YouTube Music to evaluate how leading platforms approach music sharing. While collaboration features exist, sharing is not embedded within core interaction flows, reinforcing similar off-platform friction.
Key Insight: Sharing is treated as a peripheral feature rather than an integrated interaction layer.
Spotify
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening


Apple Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening


Youtube Music
Native Sharing
Social Features
Shared Listening


IDEATION
Establishing solution architecture
I re-engaged the same twelve users in a workshop to evaluate structural approaches to in-app sharing. Flow testing clarified optimal entry points, while feature prioritization kept the solution lightweight and focused.
HMW: How might we enable listeners to share music without adding complexity or disrupting listening?
FEATURE SIGNALS
Native Solution
Sharing must be embedded within Spotify’s core listening flow.
Effortless Action
Sharing must feel immediate and does not interrupt listening.
Focused Scope
Sharing must be embedded within Spotify’s core listening flow.
EXPLORED CONCEPTS
Discarded concept explorations
Workshops surfaced concepts like persistent messaging and dedicated social layers. While compelling, they expanded scope and were not pursued. One such direction is outlined below.
SELECTED SHARE FLOW


SELECTED SHARE FLOW

JAM-SESSION CHAT
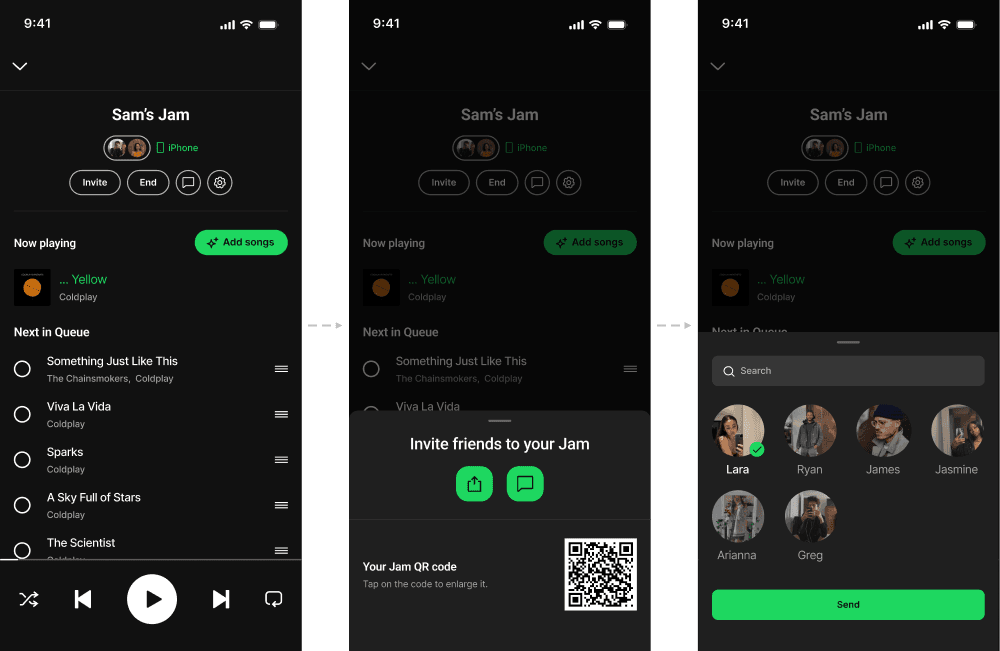

This violated the Focused Scope principle by shifting Spotify into a messaging app instead of fixing how listeners shared their music.
Testing Approach: Task-based usability testing compared time-to-share and task success against the existing flow to validate reduced friction and perceived effort.
KEY FLOWS
Integrating sharing into core flows
Sharing is now directly embedded within the core listening flow to enable fast, low-friction interaction. This shifts sharing from an export action to an integrated interaction layer.
QUICK SHARE


Quick share integrates directly into the player to enable immediate, low-effort sharing. This significantly reduces cognitive load on users.
INBOX


A native inbox creates a dedicated space for users to share music. It keeps interaction centered on music without introducing more complexity.
REFLECTION
Solving the right problem
This project reinforced solving the right layer of the problem. Sharing friction, not missing social features, was the core issue. Embedding sharing into existing flows resolved intent without expanding scope.
DISCARDED CONCEPTS